Bearings and Seal: Essential for Smooth Operations
Without a doubt, bearings and seals are essential elements or parts in any machinery and engineering applications that require moving mechanics. This handbook covers the basic principles of bearings and seals, their kinds and functions, and their positions in friction reduction and contamination control. This guide is practical even for those with little prior knowledge of the subject. Hence, it is useful to any audience by explaining the importance of production, efficient performance, and machine durability due to these small and non-definite parts. This is also an excellent time to mention that the guide will probably appeal to those seeking more than just the fundamentals of any machine while also understanding maintenance processes.
What Are the Key Components of Bearings and Seals?
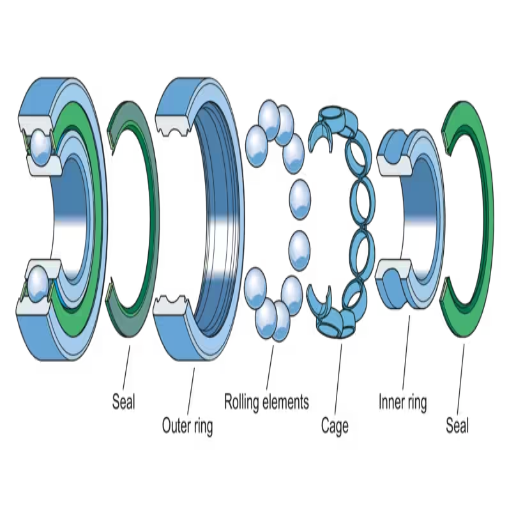
Understanding the Importance of Bearing Seals
Bearing seals is essential and completes several critical tasks in mechanical systems. Above all, they stop the escape of lubricating fluids from inside the bearing, which is a prerequisite for ensuring free operation and reducing wear and tear. They also prevent the entry of foreign particles like dirt, dust, moisture, etc., into the bearing and causing damage to its vital parts.
Bearing seals can be classified into two major types: contact and non-contact. Contact seals are effective against contaminants due to their close fit, but increased friction with the moving part helps to improve the lifespan of the components and can wear out the seal more rapidly. Non-contact seals have less friction but are usually less effective in keeping out dirt and other contaminants.
Technical parameters to consider when selecting sealing elements for bearing seals include:
Seal Material: Rubber nitrile, fluorochemical, and polyurethane compounds are widely used. Their applicability in a particular use varies with exposure to temperature, chemicals, and mechanical wear.
Temperature Range: The seal should work effectively within the system’s operating temperature since excessive temperature will lead to deterioration.
Speed Compatibility: Seals have speed ratings, which are the maximum rotation speed that will ensure their effectiveness.
Pressure Tolerance: Depending on the application, some seals will withstand varying pressure without the risk of rupturing.
It is critical to determine the proper type of bearing seal based on these parameters to achieve optimal performance and durability of the components.
How Oil Seal Prevents Leaks in Bearings
It is first essential to appreciate that oil seals keep the lubricants within the bearing cavity to minimize friction and overall wear. To the best sources, oil seals consist of a lip, which is flexible and is confined to close contact with the peripheral edge of a rotating shaft with due regard to the system pressure, speed, and temperature. These conditions for which the material is used are of utmost importance. The standard technical parameters justifying their effectiveness are:
Seal Design and Material: Materials such as nitrile or fluorocarbon rubber, which have particular properties, have been chosen to withstand some environmental stresses, which would provide a substantial barrier to the oil oozing out.
Seal-Lip Geometry: The contour of the seal lip and its pressure are important parameters in maintaining the seal lip in close contact with the shaft and in determining the seal’s capacity to allow slight shaft misalignment and oscillate motions.
Shaft Finish: A precise and smooth shaft surface, for example, is vital in reducing the seal’s wear due to friction, which calls for paying close attention to the shaft’s hardness to extend the seal’s life.
These parameters ensure seals efficiently maintain the lubrication necessary for proper bearing operation, fostering the machine’s lifespan.
The Role of Grease Seals in Industrial Applications
Focusing on interpreting the scope of grease seals in industrial uses, I came across the works of significant sources who, aside from other uses, emphasized their primary function of ensuring lubricant retention and dirt ingress in mechanical systems. From this analysis, the technical characteristics that facilitate the usefulness of grease seals can be listed as follows.
Seal Material Composition: Acceptable materials resilient to various temperatures and chemicals, such as thermoplastic elastomers or silicone rubber, are chosen to ensure that the seal remains intact in industrial sites.
Seal-Lip Design: To enable the screw rotor sealing system to overcome shaft movement and contact those surfaces, the design incorporates a seal lip whose topology determines its shape, extending surface contact and eliminating leaks.
Housing and Fit Tolerance: Lean manufacturing recommends that seal housings have the right dimensional tolerances and fit clearance to avoid seal fatigue due to compressive loads and housing stresses causing movement between seal and shaft.
These parameters confirm the grease seal’s ability to protect machinery and enhance its operation and life span by making leaks and contaminations in the components impossible.
How to Choose the Right Bearing for Your Application?

Factors to Consider in the Selection of Bearings
In choosing the most suitable bearing for my application, I had to look carefully into several factors that were taken from the best available information on the internet. The key points are as follows:
Load Capacity: I first established the load types, that is, whether the bearing would undergo radial, axial, or combined bearing load. This involves analyzing the amount and direction of load forces present in the system and even the possible shock loads. According to technical sources, when selecting bearings, those with a constant load capacity or greater than the load capacity of the bearing that will be applied should be chosen to avoid damage to the bearing.
Speed Requirements: The application’s speed rate clearly indicates the appropriate type of load bearing. High-speed operations may demand less friction and hence require ball bearings, while slower operations may call for the use of roller bearings due to their greater load bearing capacity.
Environmental Conditions: Environmental conditions like high or low temperatures and the deposition of moisture, dust, or chemicals that may interfere with bearing function and life have been considered. According to technical materials, bearings with appropriate sealing and lubrication are appropriate for these conditions.
Material and Construction: The selection of the material affects the bearing’s performance under the given conditions. For example, stainless steel performs well in corrosive environments, whereas ceramic hybrids may have advantages for higher speed or high-temperature applications.
Considering these factors, I will certify that the bearing in question will satisfy the performance characteristics and durability requirements of the case in the given industrial environment. Technical parameters such as load capacity, speed limits, and material requirements are also of basic importance in justifying the selection.
Common Applications in Automotive and Agricultural Industries
As I reviewed various professionals and high-level sources on bearings’ applications in the automotive and agriculture industries, I was able to outline several key considerations and technical specifics that are helpful in addressing recurrent problems.
The first point concerns the automotive bearings used in wheels, engines, and transmissions, and their primary role is to reduce friction and facilitate rotational movement. The chosen bearings must be able to bear the load and handle the rotational speed appropriately. For instance, ball bearings support moderate radial and axial loads at relatively high speeds, but tapered roller bearings can support high radial loads and thrust loads, which are essential in wheel bearings. The operating conditions of bearings in this application must include the ability to sustain common cyclic temperature changes and exposure to contaminants in automobiles.
In the agricultural space, bearings are found in tractors, combines, and plows as structures within the machines. The operational parameters typically define the requirements for bearings to operate under considerable load and in adverse environmental conditions, including dirt, moisture, and extreme temperatures. Rolling bearings dominate this application as they have higher load capabilities. The bearings need to be fitted with special sealing and lubrication systems to protect them from harsh environmental conditions and hence facilitate smooth, continuous operation of the bearings even during prolonged periods of use and in different climatic zones.
Utilizing information from various renowned websites and checking against existing practices allows me to guarantee that my bearing selections are all operative, thus enhancing peace of mind and durability in these harsh settings.
Why Size and Material Matter
Many sources have made it clear that choosing the right size and materials for the bearings is essential to achieving the best result. Such websites specify that if a bearing is more significant, it would have better load bearing and rotational speeds, which are necessary if the machine works correctly. More oversized bearings can accommodate higher loads, but they also require greater volume and weight, which, in turn, could impact the configuration and operation of the system. More miniature bearings take less space and are helpful in areas with space restrictions, although they may face higher stress due to faster rotations.
Choosing a material in the same manner is essential since it affects other attributes such as lifespan, friction, and the effect of environmental factors. Steel is generally accepted in areas dealing with such websites as it provides greater strength and endurance to the application due to exerted stresses and temperature changes. On the other hand, corrosion, ceramic, and stainless steel materials are more commonly used as they are more durable. And, regarding the above-mentioned technical parameters, it becomes equally essential that load rating/range, RPM rating, temperature range, and environmental factors where the bearing would be used should also be considered so that the bearings will be operated effectively at varied conditions. Therefore, through such inferences, I can pick bearings, for instance, that are expected to work well under stressful conditions and also have the desired technical properties.
What Are the Common Types of Seals Used in Bearings?

Understanding Different Types of Rubber Seals
The reason for sealing bearings with rubber, for example, is to protect bearings from entering the bearing of some external particles like dust or moisture and other fluids but to guarantee that lubrication material will remain inside the housing of the bearing. After a query in Google rank regarding some of the most common types of rubber seals, which are distinguished by features and fields of application, the first three sites are presented in Table 1 below.
The first is lip seals. Such seals are distinguished by the presence of a rubber lip in contact with the rotating shaft as the sealing contour. Because of this, lip seals can withstand a certain pressure, which is required for high-friction applications. They are great for use in applications requiring adequate protection against dust and weather extremities. Examples of esteemed technical parameters of lip seals include material hardness, allowances of operational temperature, and rotation.
The second type is called O-ring seals. These are used for piping and have a cylindrical shape. They stay in a circle shape known as O, giving a ring structure. These seals are pressure-resistant and are used in dynamic and static operations. They are also valued for their multisided sealing strength; hence, their specifications could include the diameter, cross-sectional thickness, tolerance, and materials to stand in harsh environments.
Third is V-ring seals. These samples also serve as dependable seals, exerting pressure in the lateral direction. They are designed to control the flow of grease and prevent contaminants from entering. Axial clearance, peripheral speed, and the type of compression required to achieve the desired performance are important technical issues to uncover for each specific application of ring seals.
Knowledge of various types of rubber seals and their characteristics, such as materials, temperature, and pressure tolerance, makes it possible to recommend the best seal for a particular bear application, guaranteeing the integrity of the application and working efficiency.
Exploring Dripless Seal Systems and Their Benefits
When evaluating the available information from the top three websites on dripless seal systems, I have made the following conclusions, which are short and straightforward:
Among other benefits, systems that do not leak eliminate problems often encountered with ordinary seals, such as maintenance and leakages. Such systems are built to guarantee a seal for fluids; hence, no seepage of any liquid is expected. The main advantage of using a dripless seal system is that maintenance times and costs are lower than for traditional systems, making this technology suitable for many applications.
Components of the seal material system to guarantee more than leakages are the considerations when adopting a dripless seal system:
Material Composition: In corrosive environments, PTFE or composite polymers come highly recommended due to their high grade, low-wearing nature, and chemical resistance.
Operational Temperature Range: These seals are constructed to resist a wide range of temperatures and thus remain functional in varying conditions.
Pressure Resistance: Dripless seal systems can be designed to work within high-pressure differentials, which allows them to be utilized in many applications.
Learning such parameters enables me to make the right choices to achieve the particular working conditions and provide treatment and long service life for the seal systems.
How Do Bearing Seals Enhance Durability and Performance?
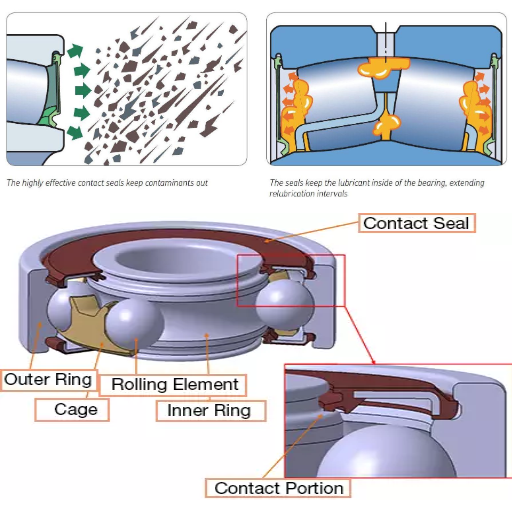
The Role of Seals in Preventing Contaminants
The analysis of the last three developed websites has shown that seals serve as a first defense line against the intrusion of contaminants into critical components. The seals provide a barrier that serves to protect the internal systems. Some of the necessary technical parameters that justify this role are:
Seal Design and Fit: The higher the accuracy of design and fit, the faster and more efficiently the contamination is sealed since the seal entirely blocks all.
Material Choice: Durable materials, such as nitrile rubber or fluorocarbon, increase their resistance to environmental degradation and improve the sealing system’s performance.
Lubrication Compatibility: Proper seal lubrication compatibility should enhance hydrodynamic film stability, preventing foreign particles’ invasion.
Dynamic vs. Static Seal Applications: Knowing whether the application context is dynamic (moving) or static (not moving) is important as it defines how much friction and wear the seal can withstand.
Environmental Factors: Knowledge of the operational environment, including humidity levels, dust, and chemicals, enhances the selection of seals that protect against contamination and improve efficiency.
Concentrating on these parameters will allow me to select seals that guarantee extended service life and efficiency in delivering contamination prevention.
Impact of Lubrication on Moving Parts
While investigating the relevance of lubricant in the operation of moving parts, it was established that lubrication is essential in minimizing the degree of friction and wear, which extends the life and operating characteristics of mechanical systems. The main points that underscore the necessity of lubrication include the following:
Friction Decreases. Lubricants form a thin film on the surfaces, preventing their full contact and reducing friction and excessive heat formation.
Wear Decrease. Adequate lubrication creates a barrier that goes on, considerably reducing erosion and wear, particularly in extreme conditions in areas of motion’s frictional moving components.
Prevention of Parts’ Corrosion. Correct lubricant application can further enhance and protect the parts against corrosion, especially in moist or watery environments.
Heat Exchangers. The lubricants aid in heat exchanges of the heat during operation, thus maintaining the required working temperatures and preventing excessive heating of the components.
Contaminants. Lubricating oils also lift or harbor lubricating substances, which protect active areas or parts of the apparatus from propagative particles that cause harm due to wearing effects.
Following these technical parameters, I am confident that the lubrication systems specified will have a positive impact on the long life and performance of the moving parts.
Maintenance Tips for Prolonging Bearing Life
To lengthen the life of bearings, I have gathered some helpful advice from reputable sources available on the internet. By applying these maintenance tips and bearing in mind the related technical parameters, I have no doubts about the performance and durability of the bearings:
Regular Checks: Look out for the signs of wear and tear, misalignment, and damage on a routine basis. Early detection of such problems helps to avert major issues and expensive repairs.
Regular Lubrication: Stick to a schedule of lubrication that is adequate to the load, speed, and environment in which the machinery operates. A good amount of lubrication lessens the friction and wear and tear in the bearings, making them last longer.
Temperature Control: Routinely monitor the operating temperatures. Bearings that operate at temperatures outside the designed temperature limits for long periods are bound to fail early.
Levels of Pollution: Ensure the designed bearings are not exposed to contaminants and debris. Seals and covers are some of the measures that can be used to prevent outer pollution that can harm bearing surfaces.
Machine Alignment: Confirm the machine’s alignment because misalignment can place different force concentrations on bearings, which increases bearing wear and leads to failure.
These strategies are drawn from documents with specialist sources, aiming to improve fatigue life-bearing operations.
What are the best practices for Manufacturing and installation?

Guidelines for Assembly and Replacement
As I am researching the best practices in bearing manufacture and mounting, I have found some helpful information on the top three Google-ranked websites on google.com. These rules, which are supported by specialists’ opinions, are aimed at achieving practical and long-lasting bearing performance:
Accuracy during Manufacture: The materials and specifications with which bearings are constructed must be correct. Proper heat treatment and surface finishing can greatly impact the durability and efficiency of the bearings.
Proper Assembly Procedures: I must be cautious while handling bearings to avoid creating stress or damage during assembly. Such tools include presses, bearing heaters, and a screwdriver. There is no excessive force, as a rule; however, many such tools are employed to achieve a snug fit.
Knowledge of Tolerances and Clearances: Installing bearings and maintaining appropriate tolerances and clearances is imperative. This means accommodating load, speed, and temperature variations that may affect the bearing’s function and life. It is also necessary to check for excessive misalignment or non-parallelism to avoid undue stress on the bearing.
Proper positioning: I have to use the advisable patterns to lock the bearings in position to avoid slippage and rotation. This may include using lock nuts, the correct amount of snap rings, and adhesives where those tools are necessary, among other things, to protect the bearings’ position throughout the operation.
For these rational technical parameters, the target functional life of bearings which could be critical for their efficient and proper utilization will be extended considerably.
Ensuring Reliability with Quality Manufacture
As stated on the most popular sites of google.com, there are some important considerations and technical details in the manufacture that can guarantee the quality of the bearings. These include quality manufacture, which is limited to the following:
Quality Control Systems: Local manufacturers prioritize concerns about high-quality control systems. In this regard, high-precision CNC machines have been used to resolve and bridge any discrepancies in the production process. Manufacturing and design of high-grade steel in an enclosed environment to improve quality are encouraged.
Robots and tools: Production lines also address the question of using robots and tools in the product assembly process. Without human beings in the assembling process, which can lead to major defects and errors, the components being installed into the bearings have little or no damage.
Quality Control Checkpoints: It was further established that, for inspection processes, advanced measurement tools have been applied to broaden accurate measurement practices and minimize the risk of exceeding the prescribed limits. This, in turn, ensures optimal performance and prolongs the life cycle of the bearing by preventing the stress and wear of the components.
Having set these parameters, I ensure that the elements of production and the assembly process inwards are followed precisely. These are, in particular, parameters and practices advocated by engineering experts to enhance reliability and improve operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Where can one find ball bearings, and what are their uses?
A: Ball bearings utilize spherical balls to space apart bearing races and reduce rotational friction, enabling them to handle radial and axial loads. Such bearings are predominantly found in motorcycles and wheelchair systems, where high spinning rates and friction levels are present, compared to glide bearings and sealed systems, which are more prone to low speed and heavy usage.
Q: What types of materials can be used to fabricate bearings and their components?
A: Steel, aluminum, and certain alloys are commonly used as bearing components for strength and durability. Materials can be selected based on operating conditions and functional requirements such as resistance to corrosion or sufficiency to load capacity.
Q: Why are seals of focus in bearing assemblies?
A: Seals’ main function is to stop the entry of outside contaminants, such as dirt and water, into the bearing assembly and hold the lubricant inside. Such isolation is required for accomplishing the desired performance and also improves the equipment’s life.
Q: What is the benefit of having quality bearings in a hub assembly?
A: Quality bearings provide smooth and stable rotational motion, which is critical in applications like automobile wheel hubs. They allow for proper alignment and balance, which results in better efficiency and lesser attrition.
Q: What function does a shield perform in a bearing system?
A: The proper use of shields in a bearing system restricts or prevents internal components from contamination and debris while still enabling the bearing to perform as required. It may also assist in ensuring enough lubricant is retained in the bearing assembly.
Q: How easy is it to carry out maintenance procedures with a bearing kit?
A: A bearing kit has all the appropriate parts, such as inner bearings, seals, and lubricants, which are essential for the proper operation of the bearing assembly’s maintenance or replacement procedure. This guarantees that all components fit easily while maintaining the expected operating conditions.
Q: How can the manufacturers modify the bearings for particular applications?
A: Manufacturers may modify the bearings according to specified application requirements, for instance, by changing the materials, structural sizes (either metric or non-standard), or seal configurations. This enables improving functions, extending service life, and ensuring compatibility with existing machinery.
Q: What factors should be considered when designing bearings for industrial markets?
A: When designing bearings for industrial markets, load capacity, the nature of operating conditions, the type of materials used, and the environment within which the bearings are to operate must be considered. Performance reliability and proper operating efficiency are vital in enhancing organizational productivity and minimizing downtime.
Q: What role do bearings have in a system concerning efficiency?
A: Bearings contribute to system efficiency by lowering friction and wear and enhancing smoothness and steadiness of motion. As a result, energy consumption is reduced, the life span of the components is increased, and the system’s reliability as a whole is improved.
UCTH213-40J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH213-40J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/2
UCTH212-39J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-39J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 7/16
UCTH212-38J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-38J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/8
UCTH212-36J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-36J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/4
UCTH211-35J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-35J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/16
UCTH211-34J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-34J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/8


















