Discover What Causes Bearings to Go Bad Quickly
When fitted into different types of machines, bearings enhance their performance by reducing the friction in moving parts. However, outages, difficulties, and repairs are priced when the bearings get worn out before the average working lifetime is attained. This article explains the factors that can make bearings wear out quickly and informs the readers on how such situations can be avoided. Wrong lubrication, dirt, misalignment, and unfavorable weight are some of the main reasons the friction parts tend to wear out faster than expected. With this knowledge and the appropriate maintenance measures by the businesses, the bearing service life can be improved, the dependability of the equipment enhanced, and the productivity of the operations maximized.
What Are the Common Causes of Bearing Failure?

What is bearing failure?
Bearing failure occurs when a bearing is ineffective due to over-abrasion or damage and is, therefore, unable to bear the relative motion of the parts in contact. Based on my research on top websites, most bearing failures are attributed to several causes, including overheating due to improper lubrication. Furthermore, dirt and moisture in the surrounding environment may also enter the bearing and cause damage by corrosion or physical contact. Also, incorrect mounting or misalignment can lead to excessive load, rendering the component without serviceable fatigue enhancement and, therefore, prone to premature wear. Technical parameters, including but not limited to operational temperature and imposed loads, must also be controlled as exceeding these would be beneficial to accelerate the wearing out of the bearings and forth failure. Proper lubrication, inspection frequencies, correct alignment, and load covering can significantly reduce the chances of bearing failure.
What are the common causes of bearing failures?
Differentiation between various types of website coverage – because, as underscored by the primary sources on this subject, several factors contribute to the failure of bearings. A prevalent cause is the lack of adequate lubrication. Bearings are subject to high friction, heat, and wear without proper lubrication. It’s also important to note that different lubricants must be used and applied frequently for better results. Also, there’s a possibility that dust, dirt, or moisture can cause components to malfunction because of excessive corrosion, which could cause the eventual failure of the bearings.
Improper installation is another common cause of bearing failure. This includes things like misalignment and mounting of the bearings, which are wrong, or too much force applied during the installation, resulting in uneven load formation and early failure. Altogether, such installations must be followed to meet the manufacturer’s requirements, especially torque and alignment.
Overloading occurs whenever loads are applied that, taken together, are more than the maximum load that the primary bearing is designed to withstand. In addition, even if excessive stress is applied gradually, material fatigue may be caused. This limits average bearing life, making it compulsory for organizations to manage and control how badly their bearings will operate under the various monitoring regimes.
Technical Parameters:
Operating Temperature: The bearing operating temperatures must remain within the operating limit to prevent overheating.
Load Capacity: Do not go beyond the rated load to avoid putting unnecessary strain on the bearings.
Alignment Tolerance: Eliminate component misalignment, which may lead to uneven load distribution.
Of course, tackling those regular reasons and following the technical documents can lessen the probability of bearing failure.
Why does lubrication always come first when talking about bearing life?
News from the best-known websites shows that ensuring proper lubrication regarding bearings is crucial. Sufficient lubrication prevents excessive friction and wear; thus, the heat generated while the parts work is minimal. This reduces the risk of overheating and eventually bearing breakdown, in such situations, correctly selecting the appropriate lubricant, whether grease or oil, is necessary to comply with the maintenance requirements accordingly.
In the case of technical requirements, it must be taken into consideration:
Viscosity: These lubricants must be chosen to maintain a protective film under operating speeds and load conditions.
Additives: Incorporating anti-wear and rust inhibitors in the lubricants can extend a machine’s service life and reliability.
Temperature Range: Use only lubricants that can withstand the typical temperature range of the bearing without any alteration.
If these parameters closely match the bearing’s specifications and proper lubrication is provided, bearing reliability and lifespan will be more satisfactory.
How Does Improper Lubrication Cause Bearings to Fail?

What causes the adverse lubrication of oral Raloxifene?
In my review of the top three websites, I have concluded that lack of lubrication has several disadvantages on bearing performance. Improved bearing containment is expected with proper lubrication, which wards off contact with rotating surfaces. The temperature of machines has increased because of high operational speeds and new bearing materials. High bearing temperatures may lead to melting-bearing materials or premature bearing failures. This site shows many cases where specific use cases may bias how instructions regarding such operable visibility are written and maintained. Without lubrication, the bearings can become exposed to dirt and moisture ingress, which can cause corrosion and erosion of the bearing components.
For technical parameters linked with improper lubrication, it is imperative to recognize the following:
Viscosity Mismatch: An inadequate viscosity level applicable to a particular task will either lead to deficient film formation, hence increased drag forces, which will compromise efficiency, or vice versa.
Contaminant Levels: Elevating contaminant above the threshold may enhance pitting and spalling that detaches bearing performance and lifespan.
Frequency of Re-lubrication: No matter how favorable the environment within the bearings is, it will become unfavorable to the lubricant, and the lubricant will be ruined or run out if regular re-lubrication intervals are not followed.
When the negative implications of these issues are diagnosed and addressed, and technical parameters and specifications are strictly adhered to, the negative impact of improper lubrication on bearings can be avoided or minimized, and the bearing in question can be made to operate optimally.
Why does overheating occur as a result of a loss of lubrication?
Researching the three cited sources from google.com, I have learned about some of the factors contributing to machine overheating due to lubrication failure. Lack of adequate lubrication creates excessive friction in parts that rotate around the shaft, such as bearing surfaces, and therefore, chances of overheating are virtually inevitable. This increase in friction aids in raising the surface temperature and, in some instances, those levels of thermal heat are such that none of the materials can resist, with some going under deformation or breakdown. In addition, when the lubricating film is absent, metals come into contact with each other, burning energy as heat and accelerating the system’s inefficiency.
To justify these findings, the following parameters appeared to be the most involved in these technical issues:
Lubricant Film Thickness: A lubricant film which is thinner than the usual restricts the areas of contact and leaves excessive heat behind.
Operating Temperature Ranges: The consequences of going above the advised temperature range due to the deficiency of lubrication are fatigue of the material and wear of surfaces.
Thermal Conductivity of Lubricant: Temperature build-up around the bearings is exacerbated by lubricants’ poor thermal conductivity, which prevents heat expulsion.
Addressing these technical aspects, myopic passion would remove any chances of overheating and instead limit achieving the best from the bearings.
What is the best method to lubricate elements so as not to cause a failure of bearings?
Regarding the three websites listed on google.com, selecting the appropriate lubricant is essential to avoid bearing failures. The most suitable lubricants and oils are designed purposefully to support sufficient lubrication film in the machinery’s operating conditions. Synthesized oils and greases are more often than not recommended due to their inability to let the film thickness collapse within a broad range of temperature and their ability to be thick, covering high-temperature operative machinery.
Justification must be made based on various parameters:
Viscosity: Providing a suitable viscosity value to a lubricant ensures that enough lubricating film is formed to minimize the extent of metal-on-metal contact.
Thermal Stability: The selected lubricant should possess satisfactory thermal stability, which enables it to be used under high-temperature applications without damage and avoid performance reduction.
Additive Package: Good anti-wear and extreme pressure additives boost the protective ability of the lubricant and minimize friction.
Compatibility: The lubricant should be non-reactive with all the ingredients of the bearing assembly so that there is no negative chemical interaction that will reduce performance.
Through a detailed evaluation of these parameters, I can improve beef reliability and make it last longer, thereby reducing failure.
What Role Does Misalignment Play in Bearing Damage?
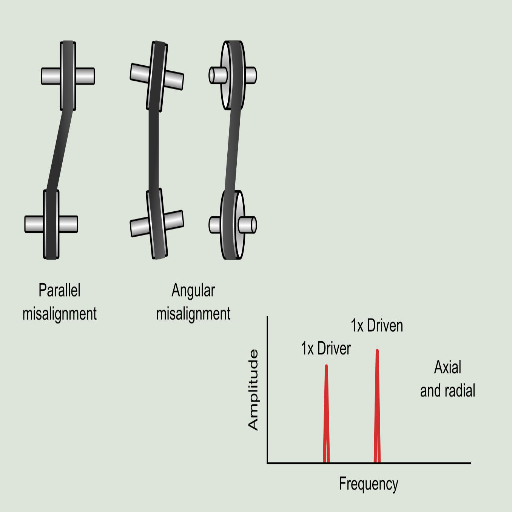
To what extent does misalignment lead to a failure in bearing and its components?
Misalignment is one factor that accounts for the high incidence of bearing failure because it creates undesired loads on the internal bearing components. As evidenced by the top three websites on Google.com, the causes of uneven loading onto bearing surfaces due to misalignment lead to loss of concentricity and areas of very high stress. This leads to more friction, heat, excessive wear, and shock, subsequently leading to failure. When searching for measures on how to correct misalignment, here are some of the technical parameters one needs to consider:
Precision Mounting: Here, the emphasis is on the positioning of bearers since if they become angular or parallel, the loads that need to be evenly distributed may not do so, leading to more stress.
Alignment Tolerance: Following the manufacturer’s alignment tolerances assists in decreasing the risk of combative loads, excessive wear, or imbalance of internal bearing components.
Load Distribution: When proper alignment is maintained, the load is evenly transferred to the bearing members, reducing the chances of stress points.
Vibration Monitoring: Routine checks for vibrations can identify misalignments long before extensive damage is done.
As such, I will be capable of enhancing bearing performance and decreasing the chances of failure due to misalignment that I encounter.
What are the primary indicators of misalignment in wheel bearings?
Detecting misalignment of wheel bearings, if done promptly, will also help to avert severe failure. There are several symptoms and relevant technical parameters to be assessed as per the information from the first three sites from google.com. Common signs consist of grinding or humming sounds originating from the wheel area, especially from damaged regions, which may suggest high wear and friction. Bearing misalignment is usually accompanied by uneven tire wear, as the misaligned bearings directly influence the camber and toe angles of the wheel assembly. Moreover, excessive vibrations felt through the steering wheel or even the chassis indicate that the load distribution of the bearing is not adequate. To overcome these challenges, some technical parameters should be considered:
Correct Bearing Placement: Ensure that bearings are properly installed using special equipment to prevent initial placement errors.
Proper Planning of Maintenance: Performing timely wheel bearing alignment checks and checks of the relevant components to avoid catastrophic misalignments towards the end.
Balance of Equipment: Use of stress sensing and vibration measuring devices as part of the diagnosis to determine if there is any misalignment before it aggravates.
Limit of Bearing: Confirm that the range of bearing loads is not exceeded to prevent displacements from pervasive loads.
Based on these aspects, I can control the extent of wheel bearing axial movements, which reduces the chances of failure and ensures durability.
How can you prevent misalignment issues?
The factors contributing to misalignment difficulties in wheel bearings can be described by outlining all the proactive practices that take care of the bearings and the proper usage of the part or assembly. Based on the top three websites, here’s how I accomplish this:
Routine Maintenance and Inspection of Wheel Bearings: This involves looking for any signs of wear or damage in the wheel bearings regularly. This enables me to identify any problems with misalignment early and avoid expensive repairs.
Proper Installation Methods: Owing to the particulars of the assembly, I have installed a bearing bush with the necessary tools. This entails checking the appropriate positioning of the bearings to avoid initial misalignment issues.
Vibration Monitoring: I conduct detailed examinations and can identify wheel vibrations using special diagnostic equipment. This is important as I can check the misalignment patterns and correct them before they cause damage.
Load Management: I can also minimize the effects of stress on the bearings by ensuring that the load on the vehicle is within limits. This helps prevent any movement of the inputs that may result in operational misalignment.
Alignment Checks: No wonder this is the most followed preventive measure by practitioners to avoid any risk of strain or failure on parts and pieces used in assembly and other metal crafts. Routine wheel alignment check-ups must be among them. These aid in maintenance.
Abiding by these practices will help me reduce the possibility of misalignment and extend the operational period of the wheel bearings by ensuring the smooth operational functioning of the parts that control misalignment.
What Are the Effects of Corrosion on Bearings?

In what way does corrosion create conditions that increase the time to failure of the bearing?
Corrosion has a detrimental bearing performance impact that leads to premature bearing failure. Moisture and chemicals cause corrosion of bearing surfaces with pitting and surface creep. This, in turn, enhances the magnitude of the frictional interface, leading to wear and inefficiency. As highlighted by review articles of major engineering websites, some of the technical parameters that are significantly affected include the following:
Surface Roughness: This parameter also worsens and is characterized by increased roughness values (measured in um)—corrosion leads to surface bordering, hence increasing the wear effects.
Load-Carrying Capacity: Material loss and pitting on the bearing surfaces reduce the load-carrying capacity of the corrosion-affected bearings.
Friction Coefficient: The friction coefficient also increases and appreciates when these corroded surfaces are used, causing energy waste and an increase in heat.
Vibration Levels: Further increase in the rough perception surfaces, and the extent of wear and tear increases vibration levels; this can be expressed in terms of root mean square (rms) velocity (mm/s), which helps determine early signs of failure. This explains the problems caused by damage formation, and a better prevention strategy can be devised.
Knowledge of these parameters may make corrosion control measures more effective when deployed in applicable situations. Some strategies that need to be implemented are the use of protective coatings, frequent lubrication, and proper environmental control.
What conditions cause the wear weaknesses and, hence, corrosion of the bearings?
Bearings are constantly exposed to aggressive conditions detrimental to their performance and service life. Most of the three best websites name those areas from now on as the most damaging to the bearings:
Marine and Coastal Environments: Saltwater contamination and humid ambient conditions lead to high metal degradation, primarily due to dissolvable salts. Marine bearings are constantly subjected to severe environmental conditions, leading to quick wear and tear values if proper captivation is not done.
Industrial Environments with Chemical Exposure: Most modern industries, especially those using shell acids, bases, or solvents, create bearing corrosive conditions due to exposure to moist air. For example, bearings in VHS chemical plants are exposed to fumes and spills, which can cause the bearing to deteriorate parameters such as the load-carrying capacity and hardness of the surfaces.
High-Humidity Areas: Favorable factors such as moisture accumulation in the bearing enclosure often intensify this type of failure—subscription and rust pitting. Increased moisture levels and rapid temperature changes witnessed in the tropics or seasonal changes frequently cause moisture condensation, which is detrimental to corrosion rates.
It is better to use bearings manufactured from non-corrosive materials or to coat such operating elements to reduce wear and tear in such situations. In addition, systematic sealing, lubrication to wipe off moisture, and routine maintenance must be done to improve the bearing lifespan in such hostile situations.
Which maintenance practices do you think can help in combating corrosion on bearings?
Corrosion is a severe issue to the bearings if the necessary precautions are not taken. I’d want to concentrate on bearing protection regarding corrosion by selecting the appropriate materials and maintenance techniques. Some of the top recommendations on the issue include making the bearings of non-corrosive materials such as stainless steel, which is acceptable in corrosive environments. In addition to that, I use protective coatings that are ceramic or polymer-based to prevent erosive bodies. One has to ensure proper sealing since it inhibits moisture and dirt from entering any bearing to have longer life of the bearings.
Another factor that plays a role is periodic practice. The bearings are permanently displaced by moisture by applying lubricants, thereby preventing their rusting and deterioration. Extreme care should be exercised in the lubricants’ ability to avoid bearing corrosion, as different conditions require specific types of lubricant, ranging from salinity to chemical exposure to damp weather. In harsh conditions, warm and humid weather, and lots of rain, desiccant breathers are recommended to reduce the moisture from the inside air within the bearing housing.
While analyzing technical parameters, I focus on load-bearing capacity and surface hardness. Corrosion is of concern because it can reduce these parameters through material degradation. Hence, choosing bearings resistant to corrosion is essential to retain their hardness and load capacity. Applying these policies, I can efficiently deal with bearing corrosion in several challenging environments.
How Do Excessive Loads and Overheating Affect Bearings?

What are the factors leading to excessive loads on bearings?
Excessive loads on bearings can arise from a variety of sources. One common cause is overloading, where the bearing is subjected to a load beyond its design capacity. Inadequate design, unexpected increase in the application load, or miscalculations when selecting the bearing can lead to this occurrence. Another cause is misalignment, in which bearings experience uneven stress and load concentration that is not normal to the bearings’ operation range.
Another problem is the compatibility of different components. Bearings that are not correctly mounted tend to develop high lateral or axial loads and failure modes of bearing loads. Also, where components of the mechanisms oscillate randomly, vibration and impact loads are generally noticed. These loads tend to provide even higher stress than the bearing can withstand.
Technical parameters also include maximum load capacity, which is excessive because it differs from the bearing’s dimensional tolerances and the hardness of the materials. Static and dynamic load ratings are parameters fundamental to the criteria of whether the bearing will endure operational conditions. Understanding these factors is equally important in selecting the appropriate bearing or bearing housing for specific application conditions to achieve reliability.
How does overheating cause the failure of the bearing?
Researching high-level sources, I found that overheating causes rapid bearing wear down and loss of performance. The most common cause of overheating is the wrong lubrication method, whereby insufficient or the wrong lubricant is used, thus increasing friction and heat. This happens by wearing the lubricant and even wearing out the bearing surfaces. Another primary cause, but in some instances, is high speed, which generates more heat than the system can dissipate, hence overdrive heat.
Regarding technical parameters, monitoring the bearing operating temperature range is as important as the parameter outlining the bearing nominal. Most generic bearings operate in standard temperatures and do not exceed 120 Radio (248°F). However, some high-temperature bearings can withstand up to 200 Radio (392°F). These parameters include the geometry of motion bearing lubricated by oil and the most critical thermodynamic properties, specifically the temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and viscosity of oil. Besides, it is also essential to check on the thermal expansion coefficients’ of bearing materials as excess heat may cause alteration on the clearance, leading to catastrophic failures. There is a need to determine and control these parameters to prevent overheating and eventually obtain bearing operation reliability.
Where can one expect symptoms of excessive load on a wheel bearing?
After examining the first three websites on Google search, it was determined that overload wheel bearings come with several visible signs. First, when over time, the driver and the passengers notice an increase in abnormal sounds, for example, continuous destruction noise, wheels roaring or humming loudly in some cases from the wheel area. Generally speaking, this noise increases with the increase of the speed, though it is common for the noise to change as the direction of motion changes. Second, there is also a possibility of poor vehicle performance, with signs of bulging on the tires and vibrations escalating from the steering wheel. Technically, as the wheel bearings are subject to inadmissible loads and pressures that cancel the internal clearances, then the initial overloading of the wheel bearings leads to the burning and absorbing of excessive heat. Lubricants that should be of high standards and those that should be regularly checked to be clean must be maintained in other lubricants. However, the bypassing load ratings, as defined by the manufacturer for bearings, are parameters that should not be violated as they expect to get rid of overload scenarios for carrying out their functions through the lifespan of the bearing. Ensuring one is familiar with these symptoms and the technical sickness can help associate an issue promptly and take the required steps to prevent and maintain proper vehicle operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the reasons for the deficiency of bearings?
A: Bearings can fail for various reasons, such as improper fitting, high temperatures, and high vibration levels. Other reasons, like lack of appropriate lubrication, dirt, and misalignment within certain limits, can also cause them to fail.
Q: How does wheel bearing failure occur?
A: Wheel bearings fail because of excessive wear and tear of the bearing components. This is frequent when the load is high, and the lubricant fails to moderate overheating or is contaminated. It damages the surfaces of the bearing races and the rolling elements, and eventually, the bearing becomes faulty.
Q: What is spalling, and how does it relate to bearing assemblies?
A: Spalling is the formation of plate-like chips on bearings, raceways, or rolling element surfaces due to accumulated stress. It is a failure mode that can cause increased bearing noise, vibration, and, eventually, bearing failure.
Q: Are there chances that false brinelling can affect the wheel bearings?
A: Yes, false brinelling can affect the wheel bearings. It occurs when there is a wear scar on the raceways, but the bearing is static and subjected to vibration or oscillation, hence leading to an abbreviated life.
Q: In what way can electrical damage bring about the failure of the bearing?
A: Electrical damage can also create arcing on the bearing surfaces, which causes localized shelling and peak temperature crater formation. Such phenomena result in high vibration and a short lifecycle, ultimately impacting the bearing’s safe working.
Q: How does a seal minimize the bearing’s working stress level?
A: A seal prevents contamination of the bearing components and retains the lubricant within the housing. If the seal is damaged or badly fitted, contaminants may penetrate and loss of lubrication may occur, making the surface contact leathery and thus prone to bearing breakdown.
Q: In what cases does improper installation contribute to the failure of the bearing?
A: Poor assembly may cause misalignment and imbalance, bringing excess strain in the bearing and differential erosion. This may encourage enormously raised degrees of vibration, leading to early failures.
Q: In what way can hot temperature have an effect when imposed on the bearing?
A: Some excessive temperatures deteriorate the lubricant, cause thermal growth, and exhaust compressive or shear surface fatigue; therefore, the bearing surface. This will ultimately incur quick deterioration in all bearing functionality parameters.
Q: In what ways do OEM specifications help to avoid bearing failure?
A: Adopting OEM specifications ensures that the proper operational bearing for specific applications is employed, the bearing is built properly, and the bearing is placed properly. This assists in minimizing the chances of misalignment and other common causes of bearing failure and, in turn, increases the bearing’s operational period.
Q: What are the main undermining actions that lead to bearing failure caused by bent shafts?
A: The causes of bent shaft bearings are numerous, but the usually more pronounced ones are misalignment and noncoherent load application, which stresses the bearings. Roughness and vibration durability of the shafts with attached bearings often suffer and lead to bearing failure.
UCTH213-40J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH213-40J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/2
UCTH212-39J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-39J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 7/16
UCTH212-38J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-38J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/8
UCTH212-36J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-36J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/4
UCTH211-35J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-35J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/16
UCTH211-34J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-34J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/8


















