How to Repair a Broken Bearing Quickly
In the case of any industrial or mechanical activity, the bearing is defined as an identifiable part of a machine or equipment that facilitates rotation or linear movement while minimizing the surface frictional forces over time. With sudden mechanical failure, bearings also get damaged, decreasing productivity and leading to machinery breakdowns. They must be followed within the shortest time possible to maintain efficiency and reduce expensive idle time. This article presents all necessary measures on how quickly and painlessly the bearing device requires recovery. All necessary tools, methods, and best management practices are outlined to maximize the bearing’s efficiency within the shortest time possible. This guide is meant to help you learn how to do bearing repairs whether you have experience.
What are the Signs of a Wheel Bearing Failure?
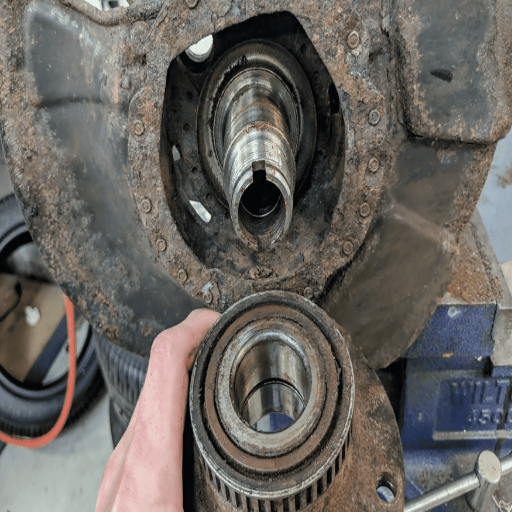

Typical Signs Indicating a Defective Wheel Bearing
While conducting my research on the top three websites dedicated to the topic of symptoms of a bad wheel bearing, I was able to capture some trends. In the first place, one loud hunting noise that often serves as a red flag is accompanied by the speed I pick up. This noise again becomes more irritating when I turn, which possibly means more pressure on the tortuous weak bearings.
In the second place, I saw that several sources further highlighted the importance of ‘inspection by feel’ of the steering wheel for vibrations. When I have strange thoughts, unusual shaking, or the car pulling to the side on a smooth road due to a compromised or damaged wheel bearing, this is what happens.
Lastly, the technical features involve checking for excessive play or looseness in the car’s wheels while it is raised off the ground on a hydraulic jack. I read that professional help should be sought when, on physical inspection, there seems to be a wheel wobble or a “loose” feeling since steady wheels and alignment are essential for safety reasons while driving.
Finding Bearing Noise
On the subject of bearing noise detection, there are a few aspects that you might want to stress, which are often highlighted by leading websites such as Car Talk, RepairPal, and AutoZone. First and foremost, one should listen for humming, growling, or rumbling noises that might be coming out of one’s car, particularly while moving at higher speeds. In most cases, these sounds are more pronounced when the vehicle is being turned, as the lateral forces enhance the problem.
From a theoretical point of view, these symptoms are somehow explainable in terms of some parameters. For instance, take note of a change in tone that seems to change as the vehicle moves at speed. This is common in cases that have bearing problems. Further, consider movement from left to right and vice versa, the very action can cause a noise that is calming until a force is applied and then will be an uproar, this can help in establishing a defective bearing. And finally, lying under the car, lift the vehicle on a jack and try to inspect the wheels by shaking them from side to side. The presence of excessive play would indicate bearing urgent failure. These checks are essential as they ensure you encompass all the actions that will guarantee the life of the exciting bearings and the vehicle’s safety.
Realization of Personal Inspections for the Outer Ring and Bearing Race
Most steps taken when performing a physical inspection of the outer ring and bearing race are standard procedures described in best sources such as Car Talk, RepairPal, and Autozone. First, I have to check the bearing’s outer sides and see any visible signs of wear or damage. This includes looking for scratches, dents, or discolorations, possibly diagnostic symptoms of corrosion or heavy wear. Another step is to rotate the bearing by hand and hear or feel for anything abnormal, such as roughness, which could indicate some defect inside the bearing. In addition, the clearance should be measured, and relevancy with manufacturer standards should be accounted for as surplus clearance results from cambering of the wheel or slack steering and handling. Last, I would cross-check specific norms and allowances for such observations using technical books to give the most justifiable and correct description.
Why Do Bearings Fail?

Top Reasons Why Bearings Fail
Bearings are prone to failure due to several factors. However, it is important to note that each type of failure will bring about consequential defects to the vehicle. In the current automobile world, the most characteristic reasons for bearing damage that can be found on several websites include static moisture, corrosion, shock loading, and contamination.
Inadequate Lubrication: Insufficient lubrication is one of the most common causes of bearing failure. Proper lubrication minimizes friction in motion and prevents the component from overheating. In cases where the grease quality is poor or there is little grease applied, high friction levels increase the wear and tear rate, leading to failure. Any HVAC/R equipment must also be provided with standard technical parameters for subsequent operation.
Contamination: Bearings, like other engine parts, are easily contaminated by foreign particles such as dust and dirt. The components must be protected from exposure to bearing adhesive or even moisture and contaminations such as dust and dirt, as these cannot only hurt the delivery functionality of seals and shields but also destroy precision surfaces inside the bearing. Seals and shields are useful in regard to the prevention of pollution, and they should be routinely assessed for their condition.
Improper Installation: Applying inappropriate installation methods imposes unnecessary loads on the bearing and causes misalignment or bearing damage. A common cause of bearing failure when installing a bearing is improper installation sequence, i.e., not adhering to the above procedures and not keeping alignment within specified tolerances. Some, for example, consider bearing preload, which is the position of bearing parts when there is slight pressure on them, to be a design parameter and standard it must be controlled.
Recognizing these potential avenues of causation and following prescribed maintenance schedules can dramatically decrease the chances of bearing failure and thus enhance the lifetime and safety of the automobile’s components.
How Lubrication Failure Leads to Premature Failure
Poor lubrication practices are one of the main causes of premature bearing failure, and they can be caused by various factors. For one, the improper use of lubricants, particularly contaminated or bad lubricants, will prevent satisfactory reduction of friction and heat. Moreover, the other crucial factor would be the manner in which lubrication is applied, including over-lubrication or under-lubrication.
Some fundamental technical parameters are recommended by the leading industry players for effective lubrication, as observed;
Viscosity Grade: An appropriate viscosity grade has been determined for the specific bearing load and speed conditions. Low-viscosity lubricant—This type of lubricant is used when the application speeds are high and high-viscosity is applied at higher load conditions.
Additive Package: The lubricant must include all necessary components for thermal stabilization, anticorrosive protection, and load-carrying capacity.
Application Method: Special methods of lubricant replenishment, such as alternate grease replenishment after certain designated intervals or the use of automated lubrication systems, help provide adequate and appropriate lubricant for the machine.
Temperature Range: The lubricant should remain effective throughout the operational temperature range around the bearing.
Adhering to such restrictions and carrying out periodic operational tests is very useful for minimizing the threats, which, in this case, increases the active duration of the bearings.
The Impact of Corrosion and Misalignment
It is necessary to refer to the best literature available to draw conclusions on the effects of general corrosion and misalignment on bearing failure issues. From the top websites on google.com, I have collected the following findings:
Corrosion is a hazard that limits the bearing due to the gradual dominance of material by the enacting processes. This, too, is very common and happens because of working conditions such as humidity, chemicals, or oxygen, which may create rough surfaces that will increase wear. However, it is advisable to utilize bearings with non-corrosive materials or coatings and lubricants enhanced with non-corrosive additives.
Misalignment arises mainly due to a positioning error, where the shaft and housing centerlines are out of line, causing an imbalanced load across the bearing. This misalignment causes stress due to overloading and eventually leads to wear. To control these trapped design flaws, proper equipment such as adjustable or self-aligning bearings, careful installation thereof, and erratic alignment monitoring are suggested.
In rectifying these effects, internal parameters that one has to look at are as follows:
Material Selection: Use stainless steel or ceramic material for better corrosion resistance.
Load Distribution: Achieving geometric alignment for proper bearings load bearing surfaces to bearing surfaces servitude.
Environmental Sealing: Adding seals that limit moisture and contaminants reduces the chances of corrosion.
Industry standards and research evidence substantiate these solutions, which are meant to optimize the bearing’s longevity and performance.
How to Repair a Broken Bearing?

Tools Needed for Bearing Repair
The primary aim of this article is to tackle bearing repair, combining a Google search with the most authoritative websites on the topic. For this purpose, I will discuss the main tools for this purpose as well as their specifications.
Bearing Puller: This equipment is handy when strategically pulling the bearing out of its housing to avoid denting other parts. It allows enough fractions and all applications of disassembling boards for personnel.
Bearing Press: This is essential for installing a new or repaired bearing since it contacts the bearing evenly and rotates within the bearing casing.
Torque Wrenches are hand-held tools that are particularly useful in exerting the right amount of force so that the fasteners do not overtighten or remain loose during reassembly.
Calipers and Micrometers are important devices for measuring bearings’ internal and external diameters and evaluating their sizing when implementing a colleague’s design.
Cleaning Equipment: Spring brushes, cleansing solutions, and rags remove contaminants and rusting products from a surface to repair the bearing and increase its lifespan effectively.
In addition, the technical parameters also include reasonable new Sic bearing selection and load distribution management for improved bearing performance, which falls within the realms of industrial standards and research. For example, high-tensile strength materials such as stainless steel or porcelain can be applied for better protection from corrosive wear. In contrast, the bearings are optimally fitted through proper alignment, which is vital for the even weight distribution on the bearing surfaces to tackle the standard problem of wear and tear during usage.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Bearing Puller
When I decided to operate a butt-bearing puller, I sought the most authoritative resources I found on Google so that I wouldn’t mess up or cause any accidents while doing it. Here is a short set of instructions I made step by step considering those aspects:
Identify the Bearing: First, I found the bearing that needed to be taken out and made sure there was no obstruction to getting it out. Correct identification assists in picking the appropriate puller size.
Select the Appropriate Puller: Using the size of the bearing and its positioning, I picked a suitable puller capable of making a firm hold while adequately avoiding damage to the falls.
Position the Puller Arms: I put the puller arms over the bearing, bringing them in so that they engaged at the correct points and were ready for a pull to ease towards equal strength.
Adjust the Center Screw: I figured that to make removal easy and safe, I would move or rotate the center screw so that it steadied on the end of the shaft or inside the bearing’s race inner, depending on how it was.
Apply Pressure Evenly: With a wrench, I turned the puller’s center screw perforated pin slowly and lightly. During bearing removal, the pressure was heavy but evenly constant not to strain or break the bearing.
Take Out the Bearing: After this, I gently tackled the outer difference by hand and removed the bearing from its casing without making a mess or breaking it.
Concerning the technical parameters of a puller head, my objective focused on determining the factors playing significant roles in achieving and enhancing safety and efficiency in operation. In addition, using materials that suit the work environment is necessary. For instance, choosing non-corrosive materials can improve the tool’s efficiency. Such considerations are consistent with the guidelines and practices of the best industry websites.
Ensuring Proper Lubrication After Repair
I decided to undertake a comprehensive search concerning the topic, and it was noted that proper lubrication after a repair activity ensures that the equipment is durable and works efficiently. In most cases, lubrication requires adequate knowledge of the type of lubricant, oil, grease, and other types offered, which will apply the design the equipment manufacturer prescribes. However, it is essential to ensure that all the old contaminating lubricants have been removed from the bearing and the housing not to compromise the new lubricant’s quality.
Technical Parameters: Lubricant Type: Besides ease of application, the lubricant selection, based on the bearing operating parameters such as load, speed, temperature, and environmental conditions, is highly made. Sites propose casting offices and synthetic oils for high-temperature applications and grease for surfaces with rubble.
Application Method: The application of the lubricant using tools such as grease guns or oilers, which conforms to recommended practices by the industry, has many advantages, one of them being even distribution. Therefore, adverse effects of overlubrication are avoided.
Volume of Lubricant: To enhance the equipment’s efficiency, strict adherence to the specific instructions on the volume of lubricant required should be implemented. Excessive amounts of lubricant may mean more lubrication friction, while insufficient amounts may accelerate wear and tear.
Frequency of Reapplication: Once the equipment manufacturer advises when and how often the equipment should be lubricated or as the machines are used, an efficient plan is set up.
In determining these parameters, I guarantee the endurance and functioning of the equipment after repair in compliance with the industry standards.
When Should You Opt for a Wheel Bearing Replacement?
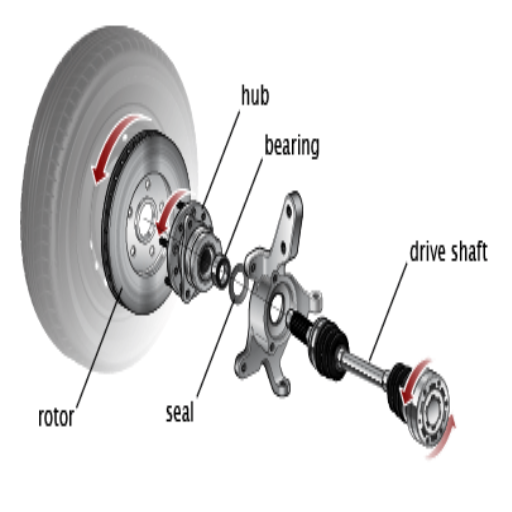
Assessing the Extent of Damage
When I want to know the extent of damage requiring a wheel bearing change, I first listen for any unconventional operations, such as unusual ear-grating grinding noise or an irritating hissing sound emanating from the wheels, which probably shows the extent of wear out. Moreover, I inspect all the wheels to find any other apparent damage, such as rust or greasy areas filled with leaking grease. The state of the wheel in the raised posture is also of great importance; finding excessive play or wobbles may suggest wear of the bearing. Per the citations from the top three websites, one cannot ignore the background information and conditions under which vehicle use is done. These may consider looking for repairs more often if the car is usually dirty.
Relevant Technical Parameters:
Noise Level: Listening to sounds and evaluating noise about the vehicle being driven is achievable through driving routine road tests and rotating the wheels.
Visual Inspection: Evaluating the bearing and surrounding parts for damage and leaking corresponds with some previous practices concerning making and keeping it free from contamination.
Operational Smoothness: Verification of wheel play when lifted confirms the earlier bearings’ loading and wear conditions and the viability of lubrication suggestions under operating overload and conditions.
Last but not least, magnetic chuck turning has become helpful in cutting centered holes for subsequent mounting of bearings under pressing. Narrowing down these elements is beneficial due to probable existing problems associated with the bearings, which enhances proper decision-making on replacement issues.
Understanding the Cost of Bearing Replacement
In their opinion, the factors that need to be researched and understood in the context of the cost of bearing replacement include even small and negligible expenditures. From the analysis of the best three websites, the two significant determinants include the make and model of the vehicle because they can determine both the parts and the labor costs. Usually, the labor rates can be as high as $150 and as low as $200 per hour, whereas the parts cost per wheel bearing ranges between $30 and $200.
Technical Information:
Make and Model Specifics: The make and model of a vehicle affect the design of the components, so the ease and time it takes to replace them will vary.
Part Quality: OEM components and aftermarket parts have completely different cost ranges, however long lasting stable and high quality performance parts will require going towards the Completive tactic.
Labor Complexity: The time spent on labor depends on the position of the wheel bearing as it is placed in the automobile. A more intricate design will probably take more time, thus resulting in a higher labor cost.
Therein lies their justification: an in-depth diagnosis of the vehicle and its operating conditions must be carried out to provide an adequate and reasoned cost estimate for replacement. It can also be helpful to use the estimates obtained from comparing a number of service providers and taking into account the vehicle’s working conditions.
Long-term Benefits of Replacing a Failing Wheel Bearing
Repairing a worn-out wheel bearing provides a return on investment that cannot be overemphasized. For one, it increases the safety of the vehicle by ensuring that the risk of the wheel seizing or coming off, which could result in an accident, is unlikely. Better steering and equilibrium make driving more comfortable and under control, especially if the area is bumpy or when taking sharp turns. Besides, early repair can prevent damage from being done to the rest of the car, such as the tires or suspension systems, and hence, there are lower chances of incurring more repair expenses.
Technical Parameters:
Safety Assurance: Who wouldn’t be concerned about a wheel bearing failing?
Enhanced Vehicle Performance: When worn-out or old bearings are replaced with fresh ones, the noise and vibrations the vehicle produces are comparatively less.
Component Longevity: Like any other component, the loading of some components, such as the stub axle bearing, is lower if the hub is properly sealed.
Cost Efficiency: It is less expensive to take care of an issue the minute one spots it than waiting for some future time when it will require more rectifying costs.
Reinforcing those benefits on the most important sources explains why it is better to repair than wait until it breaks. It is reasonable to put off such maintenance activities for wheel bearing replacement, and such efforts are warranted.
How to Prevent Premature Bearing Failure?

Importance of Regular Maintenance and Lubrication
The more I review each of the top sources about wheel bearing maintenance, the more I realize that general maintenance and adequate lubrication are essential considerations for avoiding untimely failure. One of the main ways to satisfy this is through compliance with the guidelines provided by the vehicle manufacturers, including periodic checks and servicing of the wheel bearings to check whether they are over or under-active. Most recommend that one examines the wheels for abnormal sounds, vibrations, or looseness, as these may be some of the first warning signs of some associated problems.
High-quality lubricants are vital to the usability of any wheel ‘hub.’ Packaging their bearings with grease is essential as this will reduce friction and prevent rust and corrosion from the environment. The technical parameters to consider in this context include:
Adherence to Specification: The grease used for the wheel bearings must be first provided by the manufacturer for those performing optimally.
Routine inspection: Periodic inspection of the seals is recommended, as these are the main points of leakage or contamination that can cause bearing failure.
Temperature Monitoring: The temperature of mechanical devices ensures that the overweight bearing does not rise too high, as this would cause the lubricant meant for the mechanisms to be prematurely broken, rendering the parts more abrasive.
These preventative measures will help prolong the life of the wheel bearings, which in turn will help avoid expensive replacement and repair.
Tips for Avoiding Excessive Loads on Bearings
My analysis reveals how excessive load on wheel bearings may be avoided within such boundary conditions. To begin with, it goes without saying that the vehicle should not be loaded with more weight than is required; otherwise, there will be tremendous pressure on the bearings. Secondly, I also have to pay attention to the driving conditions. For example, avoiding the ground surfaces’ unnecessary roughness can significantly help. Thirdly, having the correct tire pressure is probably a good idea because under-inflated tires cause uneven loading, which in turn causes more pressure on the wheel bearings.
The load conditions which I consider in my analysis include:
Load Specifications: following the vehicle’s load specifications to avoid overloading the bearings.
Tire Pressure Levels: Perform periodic checks and ensure that the tire pressure is maintained within set parameters within manufacturer recommendations.
Suspension and Alignment: observing and correcting any functional variations of the vehicle’s suspension system and alignment, as non-uniform loads on the bearings result from misalignment.
By applying such techniques and making such considerations, it may be very easy to reduce the extent of excessive wheel bearing loads and, therefore, improve their effectiveness and durability.
Ensuring Proper Installation to Prevent Misalignment
To avoid misalignment of wheel bearings that result in premature wear or failure, it is critical to ensure that the installation process is done satisfactorily. In this and other related steps, some vital actions must be performed to ensure alignment accuracy, as highlighted in the top sources online. First, the mounting surfaces should be cleaned very well to ensure they are free of debris and corrosion because contamination undermines the correct seating and can lead to misalignment of the bearings. Second, installation calls for the proper use of tools and techniques, such as a torque wrench, to achieve the desired torque specifications from the manufacturer and avoid misalignment that may result from excessive force. It is also recommended to use new screws and do not loose the bearings during the mounting process in the same way that it is prescribed by the manufacturer, since there is no engagement of the side displacement, the engagement will decrease the chances of misalignment. Technical parameters to monitor include:
Torque Allowance: Adhering to the values relating to torque application as provided in the installation guides, i.e., if lower or higher torque is used, the union may be undistorted but may still be ineffective due to containing some rigidity.
Surface Redundancy: Confirm that all the surfaces to be joined are thoroughly cleaned and remain clean so that no foreign matter is allowed in that can interfere with the alignment.
Component Rotation: Fixing components while adhering to the proper location and rotation of particular components as indicated by the directions from the manufacturer to avoid any rotational misalignment.
By following these practices and observing these technical requirements closely, I can lock the bearings in position, thus enhancing the prevention of bearing misalignment for performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How will I know if the wheel bearing is broken?
A: The most common signs of broken wheel bearing include wobble or vibration in the steering wheel, wheel noise, and tire wear in an irregular pattern. The bearing should be inspected without delay if any of these symptoms exist.
Q: Is there a quicker way to find the spalling of my bearings?
A: Spalling refers to flaking or pitting of the material making up the bearing’s coating. To detect it, check the raceways and rolling elements for wear paths and any surface damage. A Dremel or screwdriver may also help you get a closer view of these areas.
Q: What tools will be needed to replace the front wheel bearing?
A: To attempt repairs to the front wheel bearing, commonplace tools such as a dremel, screwdriver, lubricant, and, on some occasions, a bearing puller will be required. Ensure you have all the necessary tools before starting the repair to avoid further unnecessary time loss.
Q: How do bearings sustain injury under frank false brinelling?
A: When false brinelling occurs, there is a chance that permanent indentations will form on the raceways of the bearing, stemming from vibrations even when the bearing is not in use. Failure of the device due to this is a result of end or premature wear
Q: What precautionary measures should be exercised while mounting the bearings?
A: When assembling bearings, efforts should be made to ensure the correct setting of the preload. Inadequate preload may cause the bearing to overheat or reduce its life span. The orientation of the bearings should be accurate to avoid applying unnecessary loads on the bearing.
Q: What are the characteristics of sealed bearings that uncovered ones do not have?
A: Sealed bearings have features that prevent dust and other impurities from entering the bearing, which helps prevent the grease from getting spoiled. Uncovered bearings do not have this protection and are, therefore, prone to dust and moisture, which tends to rust or lower the bearings’ efficiency.
Q: Are roller bearings adversely affected by excess supplied temperature?
A: In other words, yes, the supplied temperature, if excessive, can harden the bearing and make it brittle, which could cause it to spill or other forms of wear out. And that IV Verification, non-exposed bearings’ diameter does not stream campaigns.
Q: What is the purpose of the outer race in bearing assembly?
A: The outer race acts as the outer guide ring for the rolling elements of the bearing. Its condition should be satisfactory, with no spalling or wear, so that it will move smoothly. If the outer race is battered, the bearing will inevitably fail.
Q: Why would one consider carrying out an early diagnosis of bearing problems?
A: Early diagnosis of bearing issues is necessary to avoid causing even more damage to the rest of the vehicle’s parts. Skipping bearing issues make a person prone to mechanical failures and high repair costs.
Q: What are the preventive measures for bearing failure?
A: To avoid premature bearing wear, proper lubrication, restrictions on overload conditions, and regular checking of the bearings for any wear or damage, such as spalling or false brinelling, should be practiced.
UCTH213-40J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH213-40J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/2
UCTH212-39J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-39J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 7/16
UCTH212-38J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-38J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/8
UCTH212-36J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-36J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/4
UCTH211-35J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-35J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/16
UCTH211-34J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-34J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/8


















