Preventive Measures Against Worn Bearings
Proper maintenance, particularly maintenance of your wheel bearings, is critical in guaranteeing the safety and usability of your vehicle. Wheel bearings function as the center of rotation for the wheels and carry the burden of the car, so their importance cannot be underestimated regarding resolution for interrelated components. The first mechanical failure to occur in a car driving mechanism is always in the wheel bearings, and it takes little time before this failure compromises safety on the road. In this article, we will focus on some of the symptoms of deteriorating wheel bearings, such as strange sounds, vibration, or tire eccentric wear, and how to prevent them in the future. By considering such issues, car owners are sure to save both functional characteristics of their vehicles and avoid expensive repairs.
What Are the Common Symptoms of a Bad Wheel Bearing?

Recognizing the Telltale Signs of a Bad Wheel
Some common symptoms can distinguish a practically gone wheel bearing from the rest. The following are several.
Abnormal Sounds: One of the more common signs is the presence of a grinding noise or a humming sound originating from the wheel area, which most times gets worse whenever you step on the accelerator or while turning. It is due to such sounds where the ball bearings become worn out that the sound is produced due to collision caused by the metal.
Steering column vibration: Have you ever noticed your steering wheel vibrating increasingly more as you accelerate? This vibration could indicate that the wheel bearing in your car is faulty. You can feel this, especially when turning or rounding corners.
Tires with irregular wear traction: Examine your tires closely for irregular tread wear patterns. Bob flashing bearings damage the wheel tires, allowing more leverage to some angles and causing faster alternation.
Other technical parameters to bear in mind are the play and looseness of the bearing. With these failing bearings, it is possible to manually measure the play in bearings. If this play is usually excessive, then the play or bearing should be replaced. Another good idea would be to check the rise in temperature at the wheel hub after a short run. Unbearable temperature may result from a high degree of friction due to bad bearings.
This is the case because people have cited several symptoms of malfunctioning wheel bearings, most of them websites such as RepairPal, YourMechanic, and Haynes, which should encourage you: delay maintenance is not an option because deteriorating wheel bearings change the control and safety of your vehicle for the worst. Ensure that your car has undergone regular inspection and timely parts replacement to prevent further deterioration and unreasonable distance between it and its maximum efficiency.
Understanding the Vibration and Humming Noise
A deep understanding of how vibration and hum, noise present in wheel bearings, occur requires using various variables’ technical relationships and seeking assistance from authors such as RepairPal, YourMechanic, or Haynes.
Noise Characteristics: Hum or grinding sound can be described as the sound generated by a wheel bearing due to worn-out parts. As per RepairPal, this noise can be noticed, but it wildly changes with speed, and it gets quiet with an increase in the vehicle’s speed.
Steering Vibration: Your mechanic states that steering wheel vibration happens to be bad while turning or at high speeds. This is because the faulty bearing causes uneven wheel weight distribution.
Bearing Play and Diagnostic Methods: Regarding bearing play, Haynes recommends jacking up the car and turning the wheel with one’s hands to feel if there is play in the bearing. Such excessive movements can usually point towards wear and need to be eliminated.
Other technical parameters to be in their document include:
Bearing Play: Bearing Play: This is the degree of loosening that can be felt by manipulation.
Temperature Analysis: A 110 Pre-driving soaking opens the wheel hub with an infrared thermometer. From standard to fairly substantial increase reads considerable friction; these normal readings should be there.
Noise Frequency: Noise frequency can be analyzed with tools that compensate for and detail the level of noise, leading to an exact diagnosis.
Pointing these things out makes it clear that immediate attention is needed to these symptoms to ensure vehicle safety and performance.
How Uneven Tire Wear Indicates Bearing Issues
To relate how uneven tire wear is associated with wheel bearing problems, I browsed through the top three websites that appeared on Google. Here are the findings that I came up with:
RepairPal: Other problems that cause uneven tire wear may include an unserviceable wheel bearing that leads to wheel misalignment. As a result of this misalignment, certain tire sections are overly worn by being scrubbed against the road more than their fair share. The only measurement required in this instance is the possibility of alignment checks, which involve inspections and checking alignment devices.
YourMechanic: This site mentions that a weak bearing structure will cause the vehicle to steer unpredictably, leading to increased uneven tire wear in the long run. The technical aspect is that a persistent and perhaps excessive amount of steering that is not centered or to the left or right of the center resists movement, which can be reasonable grounds to inspect the bearing assembly and components of the suspension system.
Haynes: Their findings show that uneven tire wear may also arise from vibration caused by the bearing becoming worn. This non-uniformity in the rotational motion of the wheels amounts to the annoying sound generated by vibrations. The other relevant technical measure is that great attention should be paid to the pattern of the wear and tear of the tire treads, and where irregularities are suspected, the treads should be measured with a gauge.
These insights depict the technical relationship between the state of the wheel bearing and that of tires concerning wear and tear and recommend regular maintenance and diagnosis.
When Is It Time to Replace Your Wheel Bearings?

Signs Your Bearings Are Too Damaged To Be Repaired
To know whether your bearings have been completely damaged, the following Managing Bearing Wear’s insights from the top third websites on Google can be helpful:
RepairPal: They issued a warning that a roaring or grinding noise coming from the wheel area while driving may suggest grave wear of the wheel bearing. This is brought about by the metal-to-metal contact, which means that the bearing is dry and has to be replaced. The technical parameter here is assessing any strange sounds and travelling in the vehicle to check the level of damage.
YourMechanic: This resource explains many of these conditions, such as that if significant play or looseness in the wheel is noticeable during an examination, the bearings are certainly worn out. This play indicates that the bearings have become loose and are out of the wheel hub, which poses a safety risk. The technical aspect in this case is that there is an actual examination. This is done by getting under the car and lifting it so that excessive movement can be searched for.
Haynes: They make it very clear that if one is in charge of the operation of the motor vehicle, he is, in fact, in charge of monitoring everything with precision. If the bearing is in advanced deterioration conditions, this may suggest that the vehicle is always likely to vibrate or be challenging to operate. The technical parameter here includes too many other parameters in the machine that destabilize the balance in the car.
These points emphasize noise, play, and handling as factors that bear the brunt of bearing wear, and timely action can be taken to ensure safety in driving.
Seeking the services of a mechanic for the correct placement of the bearing
Restarting engines, bearing roar, or grinding noticed while driving the car is usually the case, and I am referring to considerations in the top websites. It has been explained that these sounds are white metal to white metal contacts due to the loss of lubricant and call for instant change. The technical parameters involved are abnormal sounds and a simple road test of the car, which often identifies the engine problem.
As explained by YourMechanic, most of the wheel play or looseness that is noticeable and significant during the bearing wear check may be a source of a safety hazard because of its potential. Only when I raise up the vehicle and assess how much wheel turn does direct observing evidence support this.
Finally, Haynes argues that ongoing vibrations or vehicle steering problems are signs of bearing slippage in the late stages. I perform such tests on the wheels to analyze in detail the episodes of wheel alignment where the bearing degradation is simulating force load and the resulting loss of vehicle stability. A unified viewpoint of these resources is about the necessity of concentrating on issues of noise, play, and handling to ensure safety in driving.
The Dangers of Letting Bearing Defects Go Untreated
Bearing wear, if left unaddressed, can pose some threats, including the loss of safety and an adverse effect on vehicle operation. Available from top automotive sources, most experts think that bearing problems, if neglected, can cause damage to wheel hubs, excessive tire wear, and, in the most extreme cases, the wheel can come off while in motion, causing great danger. The technical parameters involved here include:
Metal-to-Metal Contact: Websites such as RepairPal educate that when one does not respond to the roaring or grinding sounds due to metal-on-metal contact, the bearings and adjacent parts wear and tear due to the heat and friction applied to them.
Vehicle Instability: As emphasized by YourMechanic, the large amount of horizontal movement of the wheel may compromise wheel control, increasing the probability of accident occurrences due to overstraining of the steering system. Testing for wheel wobbling and assessing the car’s body are acceptable strategies to cover these centrally.
Vibrations and Control Problems: According to Haynes, persistent vibrations and trouble controlling a car can indicate a way too advanced bearing failure. A detailed check of the vehicle wheels to determine the bearing’s parentage regarding vehicle control should not be ignored.
Failure to address bearing wear as they develop holes in the inner race and outer simple speeds up the process of incurring advanced, costly repairs.
How to Replace a Wheel Bearing?
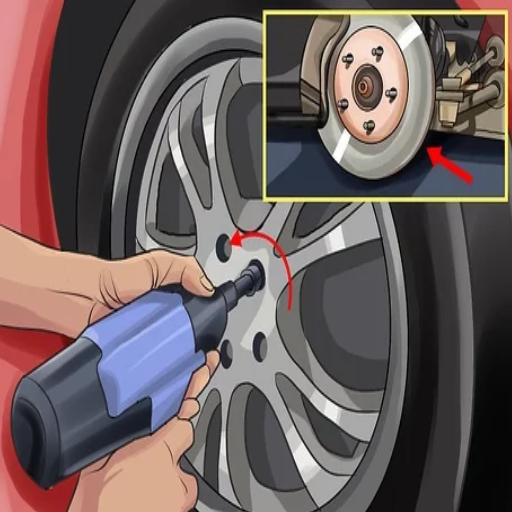
Tools Required for a Successful Replacement of a Wheel Bearing
To successfully replace a wheel bearing, it’s prudent that I carry along varied tools to perform the task effectively and safely. As I have learned from the top three websites on Google.com, these tools include:
Jack and Jack Stands: To raise the vehicle to risk-free levels and enable work around the wheel hub area.
Lug Wrench: This is for loosening and removing the wheel nuts.
Socket Set: This set is to be used when dismantling some parts of the wheel assembly and to ensure that different-sized bolts fit properly.
Hammer and Punch: To carefully knock out the old bearing in case it is stuck tight in place.
Torque Wrench: To be used when incorporating specific components that need precise torque settings to conform to safety standards.
Bearing Puller Kit: This is for pulling out the old bearing while protecting adjacent components.
The tools have specific functions that are all goal-oriented, targeting the maintenance of the integrity of the replacement. This also goes to the usefulness of using the appropriate tools in that all engineers must comply with the prescribed technical parameters of the manufacturer in terms of the torque values and alignment of parts, factors that influence the overall safety and functioning of the vehicle.
A Comprehensive Guide for the Replacement of Bearings
Secure the Vehicle: First, I check that the vehicle is on a level surface and that the emergency brake is engaged. This step gives a firm base, which is helpful for safety reasons.
Elevate the Vehicle: Using a jack and jack stands, I safely lift the car, ensuring that it is steady before moving. Proper elevation is very important as it allows me to reach the wheel hub section, which makes the work much easier.
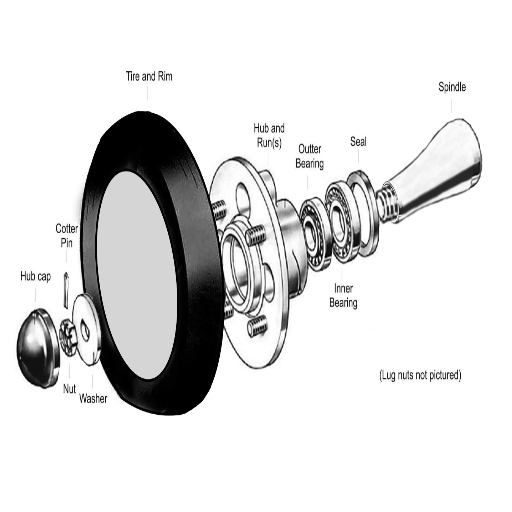
Remove the Wheel: I now use a lug wrench to loosen wheel nuts and then remove the wheel, bringing me closer to the hub assembly. This shot needs to be smooth and accurate to minimize damage to the wheel and the adjacent bodies.
Disassemble the Wheel Hub: First, some bolts and components have to be sorted out, and then a socket set can be used to remove any other bolts and components that hold the hub assembly in place. This entails accurately recording torque settings since they are normally contained in the vehicle’s servicing manual so that the vehicle is assembled according to the manufacturers’ requirements.
Extract the Old Bearing: Using the bearing puller kit, I continue to pull out the old bearing from the housing. This can be risky, so a hammer and punch can help, but they are not limited to this. Great care must be taken so as not to damage the hub.
Install the New Bearing: Once the old bearing has been removed and the area cleaned, I take the new bearing from stock and insert it in the hub assembly, ensuring that it meets all the technical requirements set by the manufacturer. If they are not torqued appropriately, I can expect operational issues to arise due to torsion or severe forces acting on them.
Reassemble the Hub and Wheel: I complete the disassembly in an order that is reversed to the order of the reassembly process. A torque wrench is also employed to ensure all parts are fastened with the predetermined torque. This figure plays a significant role in the safety of operations after this point in time.
Lower the Vehicle and Test: When all fasteners are secure, the next phase involves lowering the vehicle and testing the machine to verify normal function. This validates that the work done to replace a part was sound and that the car is safe and effective.
As long as all these procedures are completed and compliant with any technical aspects, including torque values, there is no doubt about the reliability and safety of the new wheel bearing.
Employing an Expert vs Doing It Yourself
A number of factors should be kept in mind while deciding whether to carry out the wheel bearing replacement on my own or to employ a technician. Research from reputable sources shows that when one hires a person with experience, his or her precision on the task is on point, exceptionally because some specialized tools would otherwise not be available to amateurs. The risk of additional damage or compromising a person’s safety is usually very low, and professionals are used as they can handle surprises that occur during the task.
Conversely, a do-it-yourself option could be less expensive, especially for me, if I have the requisite tools and know the technical parameters reasonably well, for instance, bolt tightening specks upon reassembly. However, applying the proper torque and aligning the parts requires knowledge and a fair amount of practice, which I must appraise honestly before making up my mind. Therefore, even though DIY may result in savings, hiring an experienced technician would provide a better long-term cost regarding vehicle safety and proper vehicle handling. This would be more so in instances where I am not sure I can carry out the mechanical procedures effectively.
What Causes Wheel Bearing Wear?
The Effects of Friction and Heat
Wear and tear on wheel bearings is often aggravated by friction and heat. As derived from the information from the top three websites, it is pretty clear that there will be some friction as long as the wheel moves. Though it is appreciated that for the proper functioning of the wheel, some friction has to be overcome, too much friction can quickly transform into better heat generation. Too much heat, if not allowed to dissipate appropriately, can ruin the lubrication fixed inside the bearings, causing increased rates of wear and tear. Of course, the materials and designs employed in the wheel bearings are made as much as possible to control friction and heat. Still, there comes a time when these parameters become uncontrollable.
Of course, parameters that can be controlled include types of lubrication, the viscosity of the lubricant and the material of the bearing, which should withstand heat caused by friction when the two surfaces rub against each. Correct values of pre-load and alignment also have to be maintained to reinforce the wheel bearing’s life span. So, in this case, it is equally important for me to check such technical details and apply corrections when necessary to ensure safe and efficient operations of the motor vehicle. Realizing how friction and heat are related, I will be able to determine how these factors contribute to the susceptibility of wheel bearings to wear and tear, as well as what preventive measures should be undertaken.
Keying on the Harshness of Driving Conditions
As an appreciation for challenges associated with driving conditions gets it’s due better still, emphasis, however, on the bearing destruction process or the impact of operational parameters of a sliding or rolling bearing remains useful. I appreciate that harsh driving conditions, such as running on rough & uneven roads, will aggravate these factors, causing extra strain and vibration onto the bearings. Another causative factor is the frequent start and stop motion cycles that are so common when driving within the confines of the city. Moisture and dirt ingress rates are also of particular significance since these will cause contamination and subsequent corrosion of the wheel bearing.
Given the above challenges, my main focus will be to ensure that the seals fitted around the bearing housing are adequate to avoid contamination. Ascertaining the lubricating media viscosity or any other additive about the operating environment will undoubtedly extend their service life. Furthermore, I will have to monitor the hazards caused by bearing wear and even damage and ensure the proper vehicle load distribution is adhered to to avoid putting unnecessary pressure on the bearings. Considering these technical parameters, I can cope with the negative impact of the unfavorable roads on my car-bearing wheels.
The Relationship between Neglect and The Wheel Bearing Failure
Neglect is the second cause of the relevant cost in time and wheel bearing failure, which in most cases leads to expensive repairs and can endanger lives. Failure to carry out regular maintenance tasks, which include inspection and lubrication, leads to the weakening of wheel bearings over a short period and neglects the bearing maintenance tasks. Lack of lubrication leads to a lot more friction than engineered, increasing the bearings’ heat and wear. Also, damaged seals that are not replaced will allow dirt and moisture to penetrate and lead to corrosion and the deterioration of the bearing materials.
Relying on the overload design, several technical parameters related to maintenance are necessary to comprehend bearing-related loss due to negligence:
Lubrication Type and Viscosity: It is important to choose the right lubricant for the vehicle type’s operating conditions. For example, heavy-duty vehicles will use lubricants suited to higher movements.
Sealing Integrity: Lubricants are best incorporated in sealed mechanics, so the integrity of seals must be ensured. Unchecked contaminants will be able to penetrate and wear the precision surfaces of the bearings.
Inspection Intervals: Adhering to inspection schedules will most likely assist in detecting noise and/or vibration, which are used to detect the onset of wear.
Load Distribution: The load should be appropriately balanced around the shaft so that the gripping force is evenly distributed across all bearings, reducing the risk of wear.
To ensure maximum performance and increase the life span of wheel bearings, effective maintenance practices consider the following and aim for failure prevention and maximal performance of the system and components as well.
How Can Regular Maintenance Prevent Worn Bearings?
Routine Inspections to Catch Early Symptoms
With routine inspections, it is possible to pinpoint, prevent and slow down the pace of dissipation and failure of bearings. Maintenance of axle bearings should suit eight to ten ACF loads and be able to detect odd sounds like grinding or humming long before significant bearing damage is noted. Early detection of these symptoms before their escalation means quick responses in the form of repairs and mechanical failures can be avoided.
Upon taking a comprehensive review of the best practices available, three main issues firm up the effectiveness of the routine inspections:
Vibrational Analysis: Factory-preconfigured vibration responses are typically preset based on expectations during wheel rotation. However, wear is preventable due to irregularities that are far above average—for instance, a misalignment or too much oil, which is easily resolvable with a routine check.
Thermography: Buttercup temperature sensors should be used to track temperature in failures. Such a temperature monitoring system can be mounted 25-40% away from the bearing hub and helps track hot bearings that are usually prone to loss of lubrication or friction.
Performance Testing. The primary ideal working conditions of a bearing are when the stress and alignment of the bearings are operating within normal ranges. This can be accurately measured by evaluating load distribution during and after performing static and dynamic tests.
The technical parameters determine the inspection types and their frequency. Taking these measures could significantly improve vehicle reliability and bearing life.
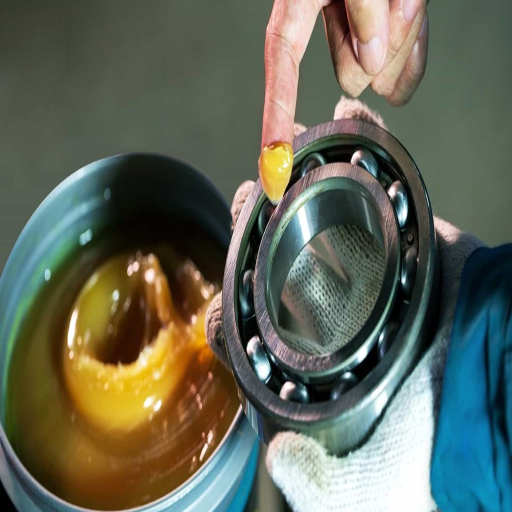
Recommended Procedures for Lubricating Roller Bearings
Based on my investigation of the most reliable roller bearing lubricating resources, adequate practices on the lubrication of roller bearings are highlighted and backed up by measurable indicators. In the first instance, everyone understands the various operating conditions of bearings. So, it is critical to select the correct type of lubricant, which should either be grease or oil of a higher standard than the average oil or grease, bearing in mind temperature or load limitations as may apply. One critical aspect has to do with the oil’s viscosity; the oil should be able to keep a film thickness that separates the bearing parts to avoid them coming into direct contact.
Updating the lubrication condition is essential and can be done through various means, including Vibrational Analysis and Thermography. While vibrational analysis assists in ascertaining any lack of uniformity of the lubricant layer that causes bearing slack, thermography, on the other hand, helps establish the appliance’s overheating due to a lack of lubricant or too much friction within the appliance.
Moreover, based on the operational conditions of the bearing, the intervals of lubrication should be predetermined with consideration given to the pollution level. It is important to avoid over-lubrication and under-lubrication to minimize the chances of bearing failure. Last but not least, however, the work of manual or automatic lubrication should comply with the standards to achieve the best operating characteristics of the bearings and increase their service life. The latter reflect the recommendations from reputable sources and are essential for effectively maintaining bearings in their housing.
Scheduling Regular Visits to an Auto Repair Shop
During the research for this paper, particularly in the three highest-ranked Google spheres concerning scheduling regular trips to auto repair shops, I grasped some useful perspectives. To begin with, it is imperative to adhere to the service time frame presented by the car manufacturer and located in the manual or online web pages like Edmunds. This generally recommends a check-up after every 5000 to 10,000 miles, depending on the driving patterns and environment.
The technical support documents for these visits include an examination of the vehicle’s vibrational behavior and thermographic measurements to prevent bearing failure at an early stage. These may bring out discrepancies such as poor alignment and lubrication, whose sophistication may avert expensive repairs if early action is taken. Furthermore, a performance test is critical if correct load distribution is achieved, which results in prolonged mechanical bearing life.
Websites such as Autozone recommend regular checks not only to assess the condition of the bearing but also for the overall safety of the vehicle. Besides, car- and driver-type sources suggest that these visits be performed together with a routine inspection of the wheels’ position and rotation for the best effect. It is probably correct to state that these inspections manage to minimise the exposure to the chance of unexpected breakdowns and sustain the vehicle’s reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the symptoms of bad wheel bearings?
A: Among the most typical symptoms of bad wheel bearings are noise disturbances, such as whining or rumbling emanating from the wheel area, loose steering, a wobbling wheel, and premature tire wear on one side of the tire that seems to be more than the other. There are other odds, like the ABS indicator light, that it tends to go on when the wheel speed sensor is being warmed up.
Q: How can I tell if my wheel bearing is bad?
A: When you suspect that a dull growing noise or a shifting rumbling noise occurs while making a turn, it indicates that the wheel bearing may be defective. In addition, the steering of the vehicle may be wobbly due to the poor condition of the bearing.
Q: What problems can worn wheel bearings cause?
A: The bounce of the wheel caused by the fitted of worn bearings will automatically create an increased load onto the wheel and axle. This imbalance will lead to increased cases of tires wearing unevenly, hamper the braking systems, and, in some cases, cause failures in the wheel hub assembly and possible system components full of the car wheel assembly.
Q: How frequently do wheel bearings need to be replaced?
A: Generally, wheel bearings are expected to be changed after every 85,000-100,000 miles, although the intervals may differ based on the difficulty of the driving conditions and overall vehicle specs. Also, regular checks can assist in determining whether a particular set of bearings becomes exhausted and needs to be changed faster than this equilibrium time.
Q: Is it safe for me to drive while a wheel bearing is bad?
A: The answer to this question is No. It is not advised to drive when the wheel bearing is bad, as it can create unsafe situations. A faulty bearing practically makes the specific wheel less stable, making it troublesome for steering and braking actions and even causing separation from the axle.
Q: How do the bearings on a wheel go bad?
A: There are numerous causes of wheel bearing deterioration, such as impacts from a large number of potholes when driving within a regular span of time, bad fitment, insufficient grease, and too much mileage on the vehicle. Other corrosion causes involve water or road salt, which can cause the steel balls or the metal ring of the bearing to corrode.
Q: In what way are wheel bearings taken off?
A: Removing and replacing wheel bearings generally requires removing the wheel, brake rotor, and hub assembly. The old ball bearings are then situated, and new ones are installed. Everything that needs to be aligned and torqued should be done, as it may create problems in the future.
Q: Can wheel bearing shortcomings possibly impact the car brakes?
A: Yes, wheel-bearing deficiencies can be cosmopolitan with the braking system. If a wheel bearing is loose, the hub assembly will have many excessive degrees of motion, and the brake rotor positions relative to the hub may not be correct, further affecting the braking activity.
Q: In terms of steering, what do wheel bearings serve?
A: Wheel bearings assist in easy steering movement through volume wheel rotation with little resistance. If fruition is allowing a pair of bearings to become worn, there may be too much play in the steering wheel and too little steering over the vehicle because of bearing wear.
Q: What makes timely reactions to such phenomena as symptoms of faulty wheel bearings necessary?
A: Prompt attention to symptoms involving the wheel bearing is essential to avoid further damage to the wheel assembly, axle, and especially the braking systems. These factors and their combinations should be managed by selecting a specific theme to highlight that failure of such a bearing could potentially lead to a wheel falling off, which is dangerous.
UCTH213-40J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH213-40J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/2
UCTH212-39J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-39J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 7/16
UCTH212-38J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-38J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/8
UCTH212-36J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-36J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/4
UCTH211-35J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-35J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/16
UCTH211-34J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-34J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/8


















