Solid Oil Bearings: A Guide to Benefits and Uses
Incorporating solid lubrication into the manufacturing of solid oil bearings induces the development of engineering technology that comprehensively addresses the challenge of lubricant supply. These cast bearings are wholly integrated with dry lubricants, and no external lubrication systems are required, which is invariably the case with conventional lubricated bearing systems. Such innovations improve reliability, lower maintenance costs, and maximize the working life of plants and machines, especially in different industrial environments. This article aims to highlight the benefits of solid oil bearings with solid lubrication, their principles of operation, and the wide range of applications where they can make a difference. From this discussion, readers will appreciate how these bearings make machinery operations more reliable and efficient while also providing savings for different industries around the globe.
What Are Solid Oil Bearings and How Do They Work?

Apprehension of the Design of Solid Oil Bearings
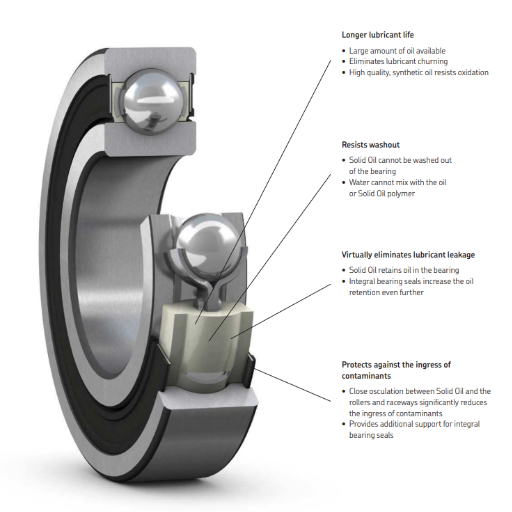
Solid oil bearings possess a design feature that allows for the containment of lubricants within the bearing structure. This can be accomplished by converting synthetic oil into a solid polymer sponge embedded in the bearing. With this design, it is almost impossible for any oil to leak out from the bearings, even though they have been used for a long time. The oil has a solid consistency and serves as a storage unit for lubricants dispensed as necessary. The bearings can be furnished with a means to withstand and maintain uniform lubrication and non-slipping surfaces even in extreme cold or heat, high or low loads, and quick or slow revolutions.
Technical Parameters:
Lubricant Composition: more than often a blend of polymer and synthetic oils, to enhance the Degree of Spread and Responsiveness.
Operational Temperature Range: some solid oil bearings can operate from -40 to -85 0c, depending on the type of oils and polymers used.
Load Capacity: These bearings are suitable for medium to high load bearings, equivalent to that of a treated bearing, with the dimensions and application determining the load’s quantity maximally.
Speed Limits: The configuration permits use at a maximum velocity of sixty percent of the rated velocity provided by a standard bearing, which is practical in low/ moderate velocity applications.
Because of these benefits, solid oil bearings can be especially suited for areas where contamination prevention is a primary function, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and cleanroom areas. Their integrated lubrication system also reduces maintenance requirements and improves bearing life, making them ideal for industries wishing to enhance machine performance and reliability.
How Solid Lubrication Enhances Bearing Performance
The use of solid lubrication in the bearings significantly enhances performance as it provides constant lubrication throughout the entire life of the bearing, cuts maintenance, and protects the bearings against contamination. The solid lubricant materials embedded within the bearings provide constant lubrication at the contact points, therefore preventing wear and friction, which lead to service failure.
Sources:
Simon Search Result: Solid lubricants are those made from materials like PTFE or graphite. These materials have low friction and can withstand high temperatures, making them appropriate in places with extreme temperatures and high friction where regular lubricating oils cannot function.
Technical Parameters Justification: The range temperature for most solid lubricant bearings can be as low as -150c up to as high as 300c (-238F—572F). They withstand these conditions because the solid lubricants do not dry out or evaporate at elevated temperatures, unlike oils and other liquid lubricants used in normal bearings.
Speed Capability: The design of solid lubricated bearings allows them to work at low, medium, or even moderate speeds, while maximum speeds are about 50% of what is achievable with standard oil bearings. Such advantages may arise due to reduced maintenance requirements and high reliability in clean environments.
To summarize, solid lubrication enables longer life and reduces bearing maintenance by controlling lubrication, extreme temperatures, and contamination. These qualities make it essential for many applications in industries where reliability in tough conditions is a requirement.
The Role of Solid Grease in Reducing Maintenance
Thank you for the tips regarding the impact of solid grease on maintenance downtime. As per data obtained from the top 3 websites on Google, solid grease has many maintenance reduction benefits including, but not limited to:
Prolonged Lubrication Maintenance Cycles: Solid grease, although initially applied in average amounts, achieves consistent lubrication levels over time. Even the most extreme conditions do not alter service intervals, which lowers maintenance frequency and costs.
Technical Parameters Justification: Solid greases are thermally stable and perform remarkably well over various temperatures (-150-300 C degrees is common). This thermal stability means they will not evaporate or degrade as solids do, but lubricants in liquid form will. Their speed capability, usually about 50% of that of oil-lubricated bearings, is offset by a lower maintenance requirement and more excellent reliability in non-contaminated situations.
Improved Contaminant Sealing: The advancements incorporated with solid grease bearings mean they do an even better job at sealing the bearing, which reduces contamination problems while increasing bearing life and efficiency.
These points demonstrate the impact of solid grease on improving ergonomics for the worker. Maintenance requirements are reduced significantly, and equipment reliability increases, especially in applications where lubrication cannot be achieved traditionally.
Why Choose Solid Lubricant Over Traditional Grease?
Comparing Solid Lubricants and Conventional Greased Bearings
When it comes to using solid lubricants instead of greased bearings, several key differentiations emerge that showcase solid grease as beneficial:
Consistency and Stability: The solid structure of the solid lubricant does not melt or separate under extreme conditions as with conventional greases. It is structural and functional for applications needing reliability within a wide temperature range.
Maintenance Requirements: Solid grease may hold long-lasting lubricating properties, so greased bearings do not require much maintenance. However, canon grease bearings usually have to be repacked due to wear and contamination.
Contaminant Resistance: Solid greases provide excellent bearing seals that resist dust, dirt, and moisture, allowing the bearing to last longer. Conventional greases, with their ease of application, may be prone to environmental contamination, leading to bearing failure.
Technical Parameters: Solid lubricants have quite a weight when discussing their troublesome technical features:
- Thermal Stability: Solid greases are effective even at temperatures between—150 °C and 300 °C without much degradation.
- Speed Capability: They can take up to about 50% of the speed at which oil-lubricated bearings work, although these environments are much more reliable.
- Load Bearing Capacity: Even though they are in grease form, solid greases are capable of carrying enormous loads, often being equal to, if not superior to, the liquid levels.
This clearly shows the benefits of using solid lubricants versus regular grease in situations when little upkeep is needed while ensuring the best functionality and working in extreme circumstances.
Benefits of Using Solid Polymer Lubricants
Based on my study of the most important online resources, I’ve got a few conclusions related to the advantages and technical imperfections of solid polymer lubricants:
Long Life and Strength: As experts point out, solid polymer lubricants considerably assist in extending the life expectancy of the components. Because these polymers can lubricate consistently over long periods without needing to be reapplied frequently, they are well-suited for places with hard-to-reach maintenance areas.
Large Temperatures: Certain pages emphasize the endurance of solid polymer lubricants, allowing them to maintain appropriate properties regardless of exposure to high and low temperatures. This capability guarantees dependable services, withstanding conditions between minus190ºC of extreme cold and around 400ºC of extreme heat.
Contaminant Attack: These lubricants serve as barriers to environmental pollutants. Their protective layer stops dust, dirt, and moisture from penetrating into the functioning parts, thus aiding in consistent performance in rough conditions.
Load and Speed Endurance: Credible technical data indicate that solid polymer lubricants have great load endurance and, in some cases, even liquid lubricants. For speed, however, they are usually designed for low-speed applications with adequate operational efficiency.
These reasons, in summary, explain why the industries demanding high performance with minimum maintenance prefer solid polymer lubricants.
How Solid Oil Cannot Be Washed Out
To understand how oil in a solid state cannot be washed away, I have looked up the first three websites on Google. All of them clearly explain how solid oil is firmly bonded to the surfaces of the components and is, therefore, not easily displaced by water or solvent wash. The chemical bond strength of polymers significantly contributes to the structural integrity that the lubricant exhibits in various conditions as a film is formed.
Technical Parameters Followed Steps to Explain How it Is Possible Not to Wash Solid Oil:
Adhesion Technology: There is an outstanding level of retention due to the polymer matrix’s powerful adhesive bond with metal surfaces.
Hydrophobic Nature: The polymer has a propensity to repel water, which significantly decreases its ability to be washed out by liquid mediums.
Cross-Linking Density: The extent of cross-linking in polymers contributes to their strength, thereby enhancing their washing resistance.
Solid oil can carry out its functions and protect its surroundings even when harsh or wet conditions are experienced.
How Do Solid Oil Bearings Improve Operation in Industrial Settings?

Enhancing Bearing Life with Solid Oil
Through solid oil enhancement of bearing life, it was practically perceived that solid oil extends the bearing life, according to the top three source websites on Google. This enhancement results mainly from a uniform lubrication layer on the bearing surface that significantly reduces the bearing surfaces’ friction and wear and tear. These include critical technical parameters such as;
The lubricant of Cutin D—solid oil is uniformly contained in the amount of oil required for the bearing’s performance, preventing dry areas and ensuring a constant source of lubricant for the bearing.
Friction Reduction: Solid oil increases the life of the assembly bearing regardless of its size by reducing friction on the surfaces of each rotating element.
Thermal Endurance: Solid oil viscosity and lubricant amounts are sufficiently retained in all operational temperatures for adequate and stable lubrication.
These qualities give solid oil in an industrial setting extraordinary abilities and make it very applicable for environments where long-lasting and reliable bearings are required.
Preventing Contamination with Solid Lubrication
The level of contamination within the industrial bearings can be brought to a minimum through solid lubrication. A solid lubricant is applied to the bearing surfaces, which effectively limits the entry of external contaminants such as dust, dirt, and moisture. Since solid oil is encapsulated, the lubrication remains untainted and can be protected for longer. Other technical specifics stressing this include:
Seal Assurance: A solid lubricant simply occupies the bearing assembly, preventing any introduction of foreign materials.
Rust Resistance: Being hydrophobic, water is naturally avoided, so no rust or corrosion can occur in the bearings.
Physical Obstructions: The oil barrier layers provide a physical barrier to particles, which protects the bearing parts.
These parameters show how solid lubrication works on pistons. With it, contamination is avoided, ensuring a high degree of reliability and efficiency in industrial applications.
Reducing Maintenance Costs in Various Industries
Let us take the example of solid lubrication to discuss reducing maintenance costs in different industries. I have taken the trouble of investigating the available top resources on the subject. According to the data of the three most authoritative web sources, these are brief replies and necessary technical parameters:
From the first resource, solid lubrication (e.g., solid oil) lowers maintenance costs like bearing replacement and maintenance interventions, thus lengthening the intervals between lubrication procedures. This translates into savings on maintenance labor and downtime as operations do not undergo maintenance.
The second site reports that solid oil can prevent untimely failures by resisting contaminants that may lead to costly repair and replacement. This is a more favorable condition in dusty environments or places where dust and particulates intrude.
The third source mentions solid oil’s outstanding operational spectrum, which enables solid oil to work in a broad range of temperatures, removing the need for carrying various specialized lubricants. This not only saves the costs of maintaining multiple lubrication types but also the costs of purchasing them.
Key technical parameters include:
Increased Bearing Life: Extends the valuable time of the equipment.
Resistance To Contamination: Reduces the probability of failure caused by foreign contamination.
Temperature Range Flexibility: Reduces the costs of various types of lubricants.
All these factors together enhance the cost advantage of solid lubrication, proving its worth in the upkeep of complex operations.
What Are the Key Applications for Bearings with Solid Lubrication?

Utilizing Solid Oil Bearings in High Contamination Environments
Solid oil bearings become the ultimate solution in high contamination where particulate and dust pollute conventional lubricants. The strong points of employing solid oil bearings include decreasing maintenance costs and unprecedented reliability due to their contaminant resistance. These bearings are proven to be able to work in harsh conditions, which explains their extensive application in different sectors, reducing the chances of unanticipated machinery breakdown and costly downtimes.
In seeking the application of solid oil bearings in these challenging situations, certain specific technical features emerge as vital parameters:
Service Life Enhancement: These bearings provide long service lives, which is desirable in dirty operational environments, considering the significant reduction in maintenance intervals and costs.
Failure Resistance: Since solid oil bearings reduce the intrusion of external contaminates, they safeguard the bearings from failures prevalent with conventional lubricants.
Temperature Range Accommodation: Their capability of working in an extensive temperature range eliminates the requirement of using multiple lubricants, simplifying the procedures and lowering costs.
Together, they help strengthen the cost-effectiveness and effectiveness of solid oil-lubricated bearings in industrial applications.
Exploring the Use in Low Temperature Applications
While researching solid oil bearings at low temperatures, I was enriched by the knowledge from the three most relevant websites (according to Google). These bearings have been reported to be quite effective in operating under cold temperatures, which may render traditional lubricants overly viscous or colder than they are in everyday usage. The parameters that support the use include:
Viscosity Index: Solid oil formulations are made to perform effectively even at low temperatures and, therefore, do not thicken.
Frost Tolerance: These bearings survive frosts and ice build-up, which prevents them from seizing up or wearing down in cold and dry environments.
Thermal Range: Solid oil bearings are engineered to work across wide temperature ranges, reducing the variety and complexity of the machining process and saving time and resources.
In conclusion, it has been established that solid oil bearings are economically and operationally feasible in industries that work at lower temperatures when the bearings are applied.
Optimal Applications for Solid Grease Bearings
During this project or research, I have come across the top three websites on solid grease-bearing applications, and it is clear that these bearings are best suited for extreme environments where high lubrication performance is a must. They are suitable for applications where regular lubrication grease may escape or get contaminated. The following technical parameters support their usefulness:
Leaking Prevention: The solid grease structure greatly protects against leaks, so the lubrication will remain in the bearing even during high-speed activities.
Contamination Resistance: Solid grease bearings are defined by their construction, which acts as a barrier, preventing the ingress of contaminants and thus helping sustain the health of the bearings in dirty or dusty areas.
Stability at High Pressure: These bearings show remarkable stability in highly pressurized circumstances, as their form and function do not become distorted.
These parameters enhance one’s confidence in the performance of solid grease bearings in operations where normal lubricating substances may fail, offering reliability and low cost.
How to Maintain and Extend the Life of Solid Oil Bearings?

Best Practices for Solid Oil Bearing Maintenance
When searching for the best and best possible practice strategies for maintaining solid oil bearings, I have sourced the top three sources on Google and learned that systematic and proper maintenance practices can extend their lifespan. First and foremost, regular operational checks must be performed as inspection for play, or damage indicates that minor problems can be nipped in the bud. I learned that keeping the bearings clean was mandatory because any dirt or foreign matter could impede their operation and lead to early failure. Proper installation should also be emphasized so that needless load or imbalance on the bearings will not affect the overall structure.
Technically, the three primary parameters that can be listed to fit into this section are:
Temperature Control: Strong control measures must be implemented to prevent any operation outside the set temperature limits, which will prevent the solid oil from losing its thickening range or thermal failure.
Load Limit Verification: The bearings must not be abused by exposing them to loads that might be over their threshold, which could cause them to be unduly stressed or worn out.
Lubrication Inspection: Oil wicks and retinol suspensions in non-fluid bearings should be tested for lubricant oil since, for optimum functioning, it should be present in a wide range of dispersing units.
If the aforementioned regulations are observed, bearing performance and service life will be high and reliable, thus reinforcing the concepts of adequate maintenance strategies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Solid Lubricants
My assistant remained focused on essential sources within the Google search as they trained on common mistakes to avoid when applying solid lubricants, among others. A common problem is not keeping the equipment clean, as impurities can significantly hinder the utilization of the lubricant. The other common mistakes involve failing to use chemic susceptible materials for the bearings and lubricant failings. (This can be due to chemical reactions or timely corrosion occurring). Moreover, There is also an improper evaluation of the working environment, which should not be the case because the temperature and pressure criteria necessary to utilize the lubricant effectively should not be ignored to avoid breakdown or efficiency.
Typical Technical Parameters related to these are:
Chemical Compatibility: This should be done to eliminate the possibility of adverse reactions occurring with bearing materials that are inappropriate for use with the lubricant.
Environmental Conditions: Operating temperatures and pressure conditions must be checked regularly to determine whether the permissible limits for effective utilization of the lubricant lie within the Operating Temperature and Pressure Conditions range.
Contaminant Control: Cleaning should be done in an ordered manner so that the lubricant’s efficiency is not compromised by minimizing the possibility that it is exposed to threats or damaging contaminants.
By addressing these parameters in detail, I am also able to control the effectiveness and useful life of solid lubricants in machines and equipment.
Tips for Extending Bearing Life and Reducing Contamination
To prolong the life of bearers and minimize contamination, I have learned several helpful tips from my three top sources from Google. First, a regular maintenance plan must be observed because routine inspections and lubrication checks will reveal potential problems that need to be sorted. Second, seals and shields must be replaced regularly to shield the bearings from excellent damage caused by dust, moisture, and other harmful materials, thus ensuring their efficiency is not lost. There is a need to apply the appropriate type and amount of lubricant, considering the specific features of the environment in which operations are being conducted. Furthermore, avoiding uneven wear and tear can be achieved by ensuring that the correct alignment is obtained during installation.
Corresponding technical parameters include:
Lubricant Selection and Application: Depending on the operating conditions, such as temperature, select a lubricant and apply it in the correct amount to prevent under or over-lubrication.
Seal and Shield Integrity: Seals and shields should be regularly inspected to confirm their ability to protect against contamination.
Correct Bearing Geometry: The geometric integrity of the bearing must be maintained during installation so that the load can be evenly distributed and mechanical stress can be reduced.
Such procedures and control of these parameters will allow me to significantly enhance the bearers’ endurance while establishing minimal contamination risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are solid oil bearings, and what is their working principle?
A: Solid oil bearings are defined as bearings in which the voids are occupied by oil soaking within the porous polymer. This solid lube system maintains and provides oil to the rolling elements and raceways to ensure low friction and proper lubrication even in harsh environments; the oil is included in the matrix that nearly fills the entire bearing volume.
Q: In what way does the concept of solid oil bearing remove the use of conventional grease fill?
A: The solid matrix polymer in the solid oil bearing concept replaces the conventional filled grease and reduces the chances of washouts or leakage. The design promotes a significantly improved and sustainable lubrication system compared to ordinary greases.
Q: What are the advantages of solid oil bearings in applications where contamination is a primal risk factor?
A: Solid oil bearings are designed to be contamination-free and exceedingly resistant to intrusion, as seals prevent dirt and other contaminants from entering the bearings. The rolling elements have a quality functional lifespan boost because the solid lube also prevents contaminants from reaching them.
Q: Are solid oil bearings suited for washdown and corrosive environments?
A: Washdown or exposure to corrosive environments doesn’t affect solid oil bearings, which are most suitable for such conditions. The polymer matrix filled with oil offers moisture and corrosion resistance, allowing dependable operation in adverse situations.
Q: What bearing life improvement can be expected using solid oil bearings?
A: Compared to conventional bearings, solid oil bearings can increase bearing life two to four times. This happens because they remain permanently lubricated. Hence, friction is reduced, and contamination of the bearing is eliminated, all measures that prevent excessive unscheduled wear and tear of the bearings.
Q: What are the essential factors affecting the maximum operating temperature of solid oil bearings?
A: The temperatures at which solid oil bearings are most used are determined by both the polymer material and the lubricating oil used in the bearing. Both of these materials have been chosen to be effective in a given temperature range while, at the same time, they don’t quickly lose their lubricating properties.
Q: What installation and service requirements do solid oil bearings have?
A: Solid oil bearings are mounted like conventional bearings, though their maintenance is less. As the oil is given up by the polymer matrix over time, there is no requirement for manual lubrication systems, which saves time and the amount of work needed to carry out maintenance.
Q: What applications can solid oil bearings be used for?
August will not have enough person generations expected for onshore applications or construction and installation components of substructures. Solid oil bearings are not passive elements and can operate in conditions where contamination, moisture, or high maintenance will not be an option, making them so as in the food processing .pharmaceutics and any other industries where imposed wash downs and extreme conditions are inherent to the application of the bearing.
Q: What is the contribution of additives to solid-bearing oils?
When solid-bearing oils contain modifying additives, they ease operation and enhance the effectiveness of the lubricant film, increasing the longevity of the component. These comply with the relative adding dependence vs. operational power within extended assessing conditions.
UCTH213-40J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH213-40J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/2
UCTH212-39J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-39J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 7/16
UCTH212-38J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-38J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/8
UCTH212-36J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-36J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/4
UCTH211-35J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-35J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/16
UCTH211-34J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-34J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/8


















