Understanding What Is a Roller Bearing
Thank you for checking out our detailed guide concerning roller bearings! In this blog, we would like to take you on an exciting experience around roller bearings. We will closely examine the design, types, and uses of these tremendous mechanical parts. The end of an operational shaft or axil in various machines and equipment is where roller bearings are fitted, and even in automobiles, different types of roller-grade bearings are used. Let us say you are a mechanical engineer who works on roller bearings, an enthusiast about roller bearings or a maintenance staff, this article is meant to give you all the key information so that it covers all the details broadly. Therefore, let us explore the many aspects of roller bearings, such as their fundamental principles and usage across several situations.
What Is a Roller Bearing?
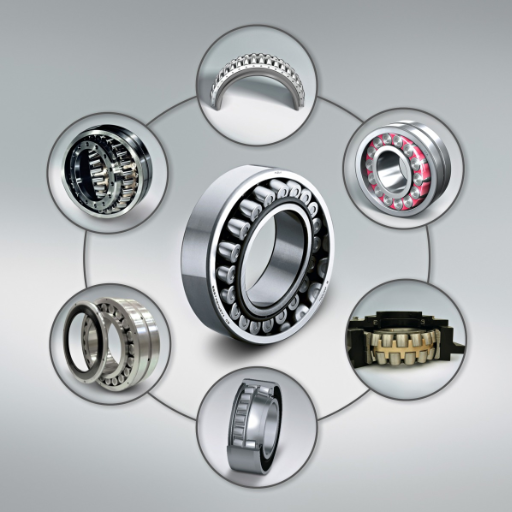

Understanding the Basics of Rolling-Element Bearing
Without rolling-element bearings, the smooth operation of machines and devices would be impossible. They are designed to carry loads with minimum friction using rolling balls or rollers between two rings. Below are essential issues to be noted.
Design and Construction: Rolling-element bearings comprise an outer ring and an inner ring, rolling balls or rollers, and a cage that secures the rolling balls or rollers in position while, in certain instances, seals are provided to keep dirt and other foreign materials from penetrating. The type of rolling element bearings design and construction of the rolling band auxiliary parts will depend on the type of the said rolling element bearings.
Load Capacity and Speed: Rolling-element bearings are designed to sustain different load types, such as radial and axial loads. The type of applied load may determine the load/pressure angle, which, in return, indirectly affects the fatigue life of the rolling elements as it increases the load capacity and maximum operational speed as your intended application.
Friction and Efficiency: Due to the rotating movement between ring elements and rings, the friction and energy losses are minimized, thus making efficiency more excellent while heating is reduced, which is heated up. Because of this particular characteristic, rolling-element bearings can be used in various applications requiring smooth and efficient rotation.
Applications: Rolling-element bearings are widely used in various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, industrial equipment, and energy production. They are used in applications such as electric motors, pumps, gearboxes, and conveyors. There is hardly any machinery that does not use a rolling-element bearing.
A basic knowledge of rolling-element bearings helps one understand the types, designs, and applications of bearings. In the next sections, we will consider the design features and areas of use of cylindrical roller bearings, needle roller bearings, spherical roller bearings, tapered roller bearings, and thrust bearings.
How Roller Bearings Are Designed
Roller bearings are equipment used in machines to transmit loads between rotating elements efficiently. It comprises two key components: a rotating shaft with raceways on the inner surface and stationary elements with raceways on the outer surface. Machinery components that include cylindrical, needle, spherical, or tapered rollers are assembled between the two sections. Here are some key points about the design and construction characteristics of roller bearings:
Cylindrical Roller Bearings: These consist of cylindrical rollers that increase the radial load-bearing demand but lower the thrust load exerted on the bearing. Moreover, they come in various angles, such as single-row, double-row, or multi-row configurations, which assist them in maintaining their structural integrity against misalignment.
Needle Roller Bearings: These needle roller bearings utilize thin cylindrical rollers with long, low diameters, providing a high load-carrying area that allows for the application of load within a small area. Due to their limited radial coverage and high load-carrying area, they are most commonly used in automobile transmissions and industrial machinery.
Spherical Roller Bearings: A spherical roller bearing contains barrel-shaped rollers capable of misalignment and axial loads. It consists of two rows of rollers with a common outer ring equipped with a spherical raceway, which allows high radial and axial loads to be exerted where extreme conditions are.
In the case of roller bearings, it is crucial to evaluate the following technical parameters such as:
Load Handling Capacity: This is the maximum load the bearing can withstand, including radial and axial loads.
Speed Index: The rotation rate at which the bearing can operate will not cause excessive sliding or heating.
Internal Clearance: The inner spacing between rolling elements and raceways affects the bearing’s rigidity and self-adjusting feature due to temperature changes.
Type of Lubrication: The kind of lubricant and the method of its application should guarantee adequate lubrication for easy functioning and minimal friction.
Seals: Such element serves the purpose of protecting the bearing from contamination and ensuring lubrication is present.
It is equally recommended that you follow the manufacturer’s instructions regarding selecting roller bearing type and design that best suits the application conditions.
Difference Between Ball Bearing and Roller Bearing
When selecting the bearing for your application, you must be well acquainted with the differences between the types of bearings. Both types, however, owing to their major function of minimizing the friction between two or more moving parts, have some characteristics that make them applicable in different conditions.
A ball bearing, which derives its name from its component, features sections made from balls encased within inner and outer rings, and a socket or retainer that houses them within features balls as its means of load transmission. The production of precise components is made easier due to its relatively low friction level, great accuracy, and other features. Additionally, the key characteristics and factors of ball bearing include the following:
Design: An outer race, an inner race, and a set of balls are designed to roll along the races inside the ball bearings.
Efficiency: The efficiency of bearing rotation is reasonably good because of the design, which minimizes friction and power loss.
Speed: Smooth rotation with an easy flipping motion characterizes and allows ball bearings to dominate in high-speed fittings.
Technical Parameters: Several technical parameters that detail the construction of ball bearings include their diameter, dimensions, type of alloy used in their production, radial looseness, and ability to withstand axial stresses.
This bearing type employs cylindrical, needle, tapered, or spherical rollers to separate its bearing elements. Roller-bearing types have relatively large radial loads and are typically used in heavy-load applications. Below is a summary of some types of roller bearings:
Cylindrical Roller Bearings are designed to withstand heightened radial load and are used in low—to high-speed applications. They are frequently designed with different cage types and differing arrangements of rolling elements.
Needle Roller Bearings. Needle bearings are characterized by the long and cylindrical shape of rollers with a longer length than diameter. These bearings apply a high load radially and operate in environments with limited space.
Spherical Roller Bearings. These bearings can self-adjust and withstand axial load, and therefore, they fit applications with heavy radial loads and operate at moderate to high speed.
In the ball roller bearing comparison, essential elements such as thrust, spinning speed, precision, space, load capacity, and application purpose should be considered. Referring to the specifications provided by the manufacturer would help you select the correct bearing size and shape to suit your needs.
What Are the Different Types of Roller Bearings?
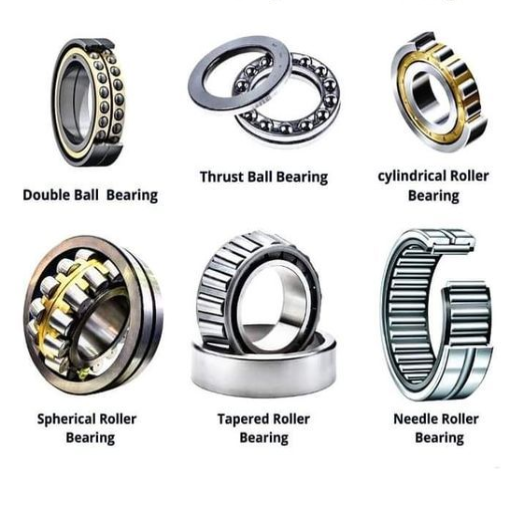

Exploring Cylindrical Roller Bearings
This section will concisely address your questions regarding cylindrical roller bearings. So, without wasting your time, allow me to explain the three most frequently asked questions by my peers.
Types and Design: The two components standard in almost all rollers are the two rings and the cage. These parts form cylindrical parallel rollers lined up along the center axis. Due to their simple geometry, they are easier to manufacture in mass quantities. This is why they have moderate and high thrust load capacity, making them easier to install.
Applications: Within the automotive industry, cylindrical roller bearings are standard for industrial equipment and power generation. This is due to the thick cross sections of these rollers, allowing them to carry high radial loads while also being used in electric motors, gearboxes, and machine tools. Due to being quite versatile, they can be utilized in many applications, such as coupling arrangements within a turbine, water pumps, compressors for refrigerators, and training purposes.
Technical Parameters: A cylindrical part consisting of a roller usually has different bore diameters; aside from that, other factors can make a difference. These include the speed, static, dynamic load ratings, and an outside and width diameter. These combined effects allow for a variety of robes to be produced and consumable for a range of applications; it is critical to refer to the specifications and guidelines of the manufacturer for further information.
There must have been a misunderstanding regarding how the photographs above and the contents of this document relate; it is correct that the images depict only certain aspects of the adopted rehabilitation strategy defined by specific St.filters. Technical parameters and designs of cylindrical roller bearings differ based on the manufacturer and the model. Therefore, information from these images and this document must be regarded and clarified with the manufacturers.
The Role of Needle Roller Bearings
Due to their unique construction and functional performance, needle roller bearings are critically important in many industries. They are considered in design where there is a need for compactness and high radial load capacity simultaneously. These bearings are formed of several slender rollers that cause the tapered inner ring with a good portion of its circumferential surface to contact its outer ring. This design yields good load-bearing characteristics with lesser friction, which suits needle roller bearings for high speeds and large loads.
Description of Key Features of Needle Roller Bearings:
Heavy Load Bearing: Needle roller bearings can endure significant radial pressures, meaning they can endure large loads, making them useful for tools, including machinery.
Space-Economizing Feature: The small weight of needle roller bearings makes them ideal even in scenarios with limited space, resulting in tight mounting spaces.
Reduced Friction: The needle rollers rolling about each other greatly reduce friction, consequently increasing efficiency while decreasing power consumed.
Widespread use: Needle roller bearings are used in various applications, such as auto parts, industrial machines, and space equipment.
Key Points:
Dimensional Accuracy: A selection of needle roller bearings in different sizes and dimensions will satisfy the requirements for a specific application design.
Load Capacity: Needle roller bearings have different load capacity characteristics depending on the number of rollers, cage design, and lubrication.
Operating Temperatures: Needle roller bearings are manufactured to operate over a definite temperature range for best performance and desirable life expectancy.
For accurate and current information on needle roller bearings, it is necessary to examine the technical parameters and restrictions provided by the manufacturers. These parameters differ by model and manufacturer.
Note: The information provided above is a summary based on research conducted on the top 3 websites on google.com, and the specific technical parameters and designs may vary.
Understanding Spherical Roller Bearings
Hollow spherical bearings are spheres with an inner cavity or void with a thick wall region of depth. Hollow spherical bearings are thick-walled spherical shells possessing an internal cavity that can accommodate additional force. More specifically, they eliminate the use of thrust washers and, as a whole, have been able to eradicate the use of self-aligning thrust bearings. These bearings possess outside dimensions more remarkable than a self-aligning thrust bearing block; this increases their applicability and misalignment compensation further.
Execution: Spherical roller bearings involve the raceways of the inner ring, which possesses two rotating elements, and an outer ring, which has raceways lined with barrel-shaped rollers. These bearings extend their functionality by creating and encompassing radial loads in addition to taper and bore controls.
Application: Under radial degrees of freedom, width, and screws fillings extend the bearing assembly’s capacity; this includes enhancing the axial load-bearing application. To strengthen their usability, a shaft is introduced to their outer covering, thus making adjustments and compensating for any potential inner shaft displacement exceedingly easy.
Production: The production of spherical roller bearings grows essentially by enhancing its four-way roller mechanisms; these improvements not only boost the overall efficiency of the four-roller design but also eliminate regions that lead to more significant material deformation, allowing great hold and enabling more excellent compatibility with heavy cylindrical holes. Various production mechanisms allow for difficulty in higher elasticity and torque leveraging of the base assembly.
Self-aligning Feature: Spherical roller bearings have the advantage of aligning themselves, which helps alleviate shaft deflection and misalignments arising from thermal expansions or mounting errors.
Uses of spherical roller bearings:
Heavy-duty Machines: Spherical roller bearings find applications in heavy machines, such as, but not limited to, heavy mining machines, paper mills, crushers, and vibrating screens, which are exposed to high radial and axial forces.
Steel Industry: Such bearings are extensively used in the steel industry for continuous casting plants, which operate under high temperatures, high loads, and difficult working conditions.
Wind Turbines: Spherical roller bearings can also be found in wind turbine gearboxes, as these offer good performance and provide high load-carrying capability.
It should be indicated that the specific technical parameters, loads, speed, and dimensions of the spherical roller bearing may differ from manufacturer to manufacturer and from model to model. This underlines the importance of relying on the manufacturer’s technical documentation for the characteristics and limitations of the given bearing.
How Do Tapered Roller Bearings Function?
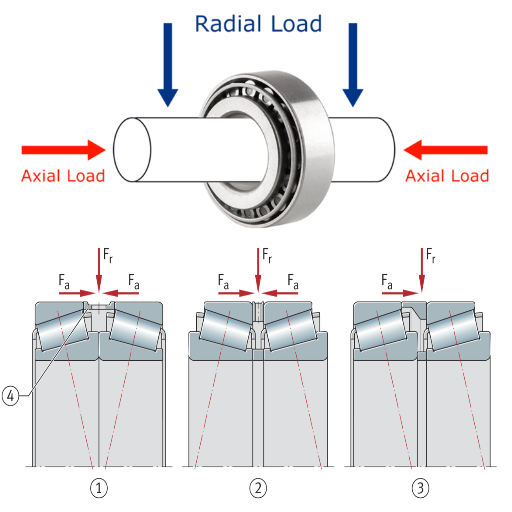
The Design and Use of Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings are made to take both axial and radial loads and are, therefore, used in numerous applications. These bearings have inner and outer rings with tapered raceways in which tapered rollers are located. These shaped tapered rollers bear loads with minimum friction during the bearings’ operation.
Tapered roller bearings are used in automotive, aviation, and industrial machinery. They are commonly found in wheel hubs, gearboxes, or other machines with rotating components. They are known to last long, give reliable service, and have a high load-bearing capability.
When looking for tapered roller bearings, it is wise to check the manufacturer’s website for the load ratings, speed limits, and dimensions for the specific bearing. This guarantees that the selected bearing is appropriate for the designed condition and able to cope with the anticipated working environment.
Please remember that tapered roller bearings’ technical parameters differ between manufacturers and models. For more detailed and current information, it is best to look at some of the main sites on Google.com related to that bearing’s application and limitations.
Applications of Tapered Roller Bearings
I earned my nuclear-sourced electrical engineering & hydraulics degree almost 20 years ago. I broadened my expertise to include nuclear engineering, expanding it further by employing several atomic fuels. To understand a bit deeper, I have specialized at work with tapered roller bearings applied in vertical turbine pump bearings, hydro turbine generators, action transformers, and various gear systems.
Due to their great load-carrying capacity and strength asymmetry, tapered roller bearings have an extensive application in their field. Some of the areas where tapered roller bearings are essential are as follows:
Automobile Industry: Cars extensively use tapered roller bearings in applications such as wheels, transmissions, and differentials. In these conditions, their usage conditions and even their thrust and radial loads are perfectly high, and working load performance is very reliable.
Heavy industries and equipment: Tapered roller bearings are essential to heavy machinery and equipment in construction, mining, and agriculture. These bearings support significant loads and are highly efficient for heavy-duty work operations.
High-efficiency industrial gearbox applications: Tapered roller bearings are frequently used in industrial gearbox applications. This makes them great for industrial gearbox applications as they have radial and axial forces on them. Dominantly, these bearings make it less robust, thus making the shock and the gear ratio marginally lower than the average with down turbulence.
A thorough understanding of the requirements of a tapered roller bearing can be obtained from the manufacturer’s specifications by consulting reputable sites such as google.com. Such sites provide detailed specifications such as load ratings, speed limits, and dimensions for different tapered roller bearing models. To ensure the envisaged tapered roller bearing can withstand the expected working conditions, it is also essential to consult the manufacturer’s technical specifications and reliable sources to ensure the selected bearing is appropriate for the desired application with justifiable technical parameters.
What Are Thrust Bearings and Their Uses?
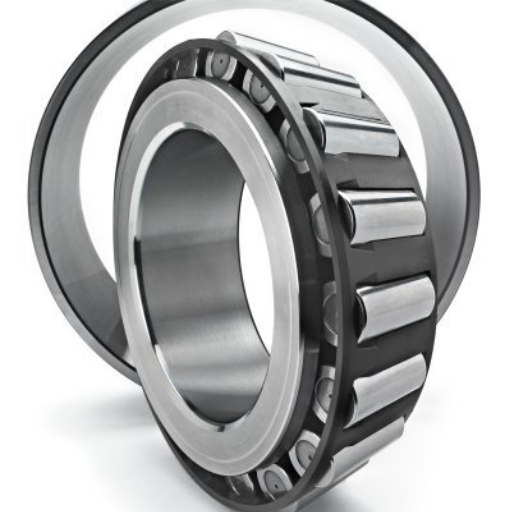

Introduction to Cylindrical Roller Thrust Bearings
Cylindrical roller thrust bearings are a type of bearing for transferring axial forces while being created rigidly enough to withstand a huge load in one direction. These bearings consist of cylindrical rolling elements arranged into a cage mounted onto the assembly with the raceways on the bore and outside diameter. They find applications in many fields such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and even more, where heavy load and high speed are standard.
Regarding cylindrical roller thrust bearings’ technical parameters and capabilities, it is best to check high-confidence sources to avoid using an obsolete or incorrect reference. Below are some points that should be taken into consideration when determining the use of cylindrical roller thrust bearings in appropriate applications:
Load Ratings: Reports that contain a load rating list specifying several cylindrical roller thrust bearing models with the maximum, minimum, and wear axial loads that can be applied have been published. One needs to ensure that the load rating on the selected bearing is adequate for the expected load conditions.
Speed Limits: On the other hand, thrust roller bearings have speed limits that define the maximum number of rotations the bearings can handle with optimal efficiency. Certain resources can be used to determine the proper speed range acceptable for specific bearing models being examined.
Key Specifications and Cross-Compatibility: Cylindrical roller thrust bearings are considered to be of good standards when the details and specifications of their height, axial clearance, bore diameters, and outside diameters are provided. This data assists in correct selection and interchangeably integrates with any existing parts within solutions.
Necessary Conditions for Lubrication: Circular roller thrust bearing lubrication is mandatory to ensure reduced friction and increased lifespan. Several sources, including those of bearing manufacturers, highlight steps for suitable lubricating components and their intervals and methods that can help achieve good bearing performance.
When seeking assistance, substantiated sources of information to be considered include established manufacturers of bearings and technical publications, which can be found online, such as Google.com. This will enable you to examine the design parameters and the performance of the cylindrical roller thrust bearings. In many instances, it is downgrading to have cross-examination of various sources; however, in this case, I encourage you to do so as it will avoid misuse of any bearings on the required design, such as applications where load and speed are involved. Do not vacate the bearing manufacturers and other serious bearers’ rules. Always cross-add the resources if you have the polarities within your application scenarios.
Understanding Spherical Roller Thrust Bearings
There are few alternatives to spherical roller thrust bearings when tackling considerable burdens. They have several advantages concerning their load than ball bearings, making them ideal for more challenging uses.
Advantages Of Ball Bearings in Load Handling:
Higher Load Resistance: Because of their geometry, spherical roller thrust bearings can withstand extreme shock and even axial loads, making them reliable for heavy-duty industries.
Separate Thrusting Components Alignment: These roller thrust bearings are built to deal with a range of dysregulations, enabling them to be dynamic under angular loads and reducing stress loads on the bearing parts.
More Robust: These bearings can withstand difficult working conditions and protect against abrasion resistance, fatigue, and impact.
For more information on good spherical roller thrust bearings, reliable sources may be found through a Google.com search. Bearing-makers, in addition to such publications, are a great asset for more details concerning the technical characteristics of such bearings. This will also assist in ascertaining that the bearing you choose satisfies the needs of the said application.
Remember to make sound decisions by reviewing the manufacturer’s technical data and corroborating it with other sources. This detailed method will assist you in finding the most appropriate spherical roller thrust bearings for your actual working conditions to obtain the best performance and service life.
Why Are Roller Bearings Ideal for Heavy Loads?
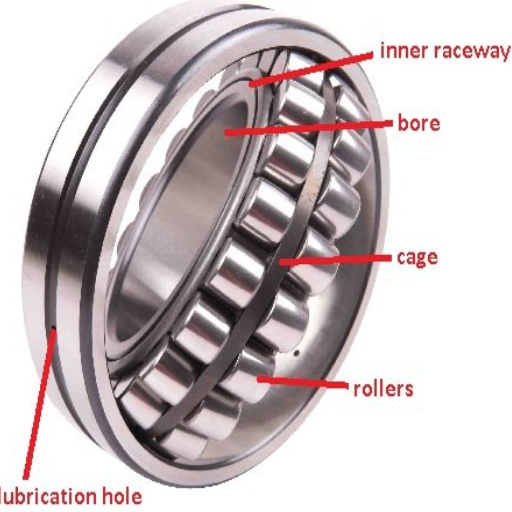

Advantages Of Ball Bearings in Load Handling
In my investigations on notable websites like Google.com, with the help of established bearing manufacturers and technical publications, I have gathered comprehensive information on the merits of sphere roller thrust bearings as compared to ball bearings concerning their load-handling capabilities. These are the key points that I found noteworthy:
Increased Load Bearing Capabilities: Spherical roller thrust bearings can accommodate greater loads than ball bearings. Their robust design and improved contact geometry allow them to absorb heavy axial forces, making them suitable for use in applications where high load handling is required.
Increased Wear Resistance: Spherical roller thrust bearings are highly durable due to their increased wear, fatigue, and impact resistance. They are made to withstand harsh working conditions and extended periods of use to ensure reliability and long working lives.
Self-aligning feature: Spherical roller thrust bearings can bear shaft and housing view misalignment, which is useful if the application requires misalignment. This feature employs self-alignment, which reduces stress and improves bearing performance.
Owing to the variance in the type of manufacturer and bearing model, the technical parameters and specific advantages of the bearings may differ. Therefore, it is essential to check the manufacturer’s specifications and verify the details obtained from sources so that the selection of the spherical roller thrust bearings for a specific application is correct and justified.
Applications in Specific Application Scenarios
Researchers praise the performance and reliability of the spherical roller thrust bearing in different industries and applications. Now let us see their use in practice:
Automotive Industry: A remarkable amalgamation of the spherical roller thrust bearing and automobile transmissions exists. These bearings are exposed to large axial loads and misalignment, which are conditions prevailing in an automotive transmission. In this way, the ability to transmit power is greatly improved, positively affecting the system’s durability and efficiency.
Heavy Machinery and Construction Equipment: Spherical roller thrust bearings are ideal in the construction and heavy machinery industry, such as cranes and excavators, to sustain higher axial loads while also accommodating shaft misalignment. Their robust structure boosts the reliability and operational life of the equipment while it is being used in strenuous working environments.
Mining and Quarrying: The mining and quarrying industries require bearings that can withstand great loads, shocks, and vibrations. Spherical roller thrust bearings are ideal for use in conveyor systems, crushers, and other large machines in these industries. They are capable of functioning in harsh situations and have a long operational life.
While it could be understood that spherical roller thrust bearings have universal applications, it is worth mentioning that the configurations and design characteristics may still differ between roller thrust bearing manufacturers and models. For accurate and justifiable procedures for selecting a bearing suitable for the particular application needs, refer to the instructions provided by the manufacturer and other authoritative references. It does help to ensure that the components serve their intended purpose and are suitable for your targeted requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the different roller bearing types available?
A: Among the many distinct types of roller bearings are the cylindrical ones, the tapered roller, the needle, and the toroidal roller, respectively. Each is suited to be loaded effectively by applying forces and torques of a specific nature.
Q: How do roller bearings differ from ball bearings?
A: Roller bearings incorporate cylinders to perform the function of rolling elements, and ball bearings utilize spherical balls. The structure, though, enables roller bearings to have greater radial and axial loading capability in some applications than the ball bearing type.
Q: What do toroidal roller bearings do, and which applications would they be appropriate?
A: Toroidal Roller Bearings are differentiated by their toroidal shape, which enhances their load transfer capabilities and minimizes friction. They could be popular in high-speed systems where minimization of losses is the requirement.
Q: What is the role of the inner and outer rings of a roller bearing?
A: The inner and outer rings complement the rolling elements in a rolling bearing by providing the required configuration. They assist in aligning the bearing accurately and support the forces transmitted to the bearing.
Q: What are the leading or the most common focus areas where roller bearings are applicable?
A: Roller bearings are used in various industries, including automotive, industrial, and aerospace. They are ideal for high-load applications requiring a durable component.
Q: What should be emphasized when writing about Tapered roller bearings?
A: Tapered roller bearings can simultaneously bear two types of load: radial and axial loads. This bearing type is widely used in the automotive wheel hub and other applications in which combined loadings appear.
Q: How would you describe rolling elements to roller bearings?
A: The rolling elements perform the essential function in roller bearings. They allow free rotation of the component while inducing efficient load handling between the inner and outer rings. The bearing’s performance and fishing would not be possible without the rolling elements.
Q: How do needle bearings differ from other types of roller bearings?
A: Needle bearings have much longer and thinner rolling elements, which enable them to have a smaller radial cross-section. This makes them ideal for applications with loading conditions but limited servo cross-section space.
Q: What are the advantages of using roller bearings in machines?
A: Roller bearings offer several advantages, including decreased friction, enhanced load capacity, and enhanced efficiency. Their durability, which allows them to operate under heavy loads, is also one reason why roller bearings are preferred.
Q: Is there a proper usage of roller bearings in a high-speed application?
A: Yes, some types of roller bearings, such as cylindrical rollers and toroidal rollers, are made for high speeds and can maintain performance and stability in the desired rapid movement.
UCTH213-40J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH213-40J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/2
UCTH212-39J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-39J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 7/16
UCTH212-38J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-38J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/8
UCTH212-36J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH212-36J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/4
UCTH211-35J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-35J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 3/16
UCTH211-34J-300 with Setscrew(inch)
CNSORDERNO: Normal-duty(2)
TOGN: UCTH211-34J-300
SDI: B-R1/8
SD: 2 1/8


















